Evaluation of cancer outcome assessment using MRI: A review of deep-learning methods
- PMID: 36105425
- PMCID: PMC9459949
- DOI: 10.1259/bjro.20210072
Evaluation of cancer outcome assessment using MRI: A review of deep-learning methods
Abstract
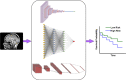
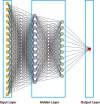
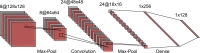
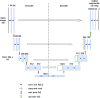
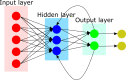
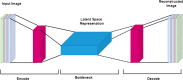
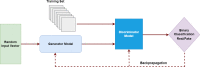
Accurate evaluation of tumor response to treatment is critical to allow personalized treatment regimens according to the predicted response and to support clinical trials investigating new therapeutic agents by providing them with an accurate response indicator. Recent advances in medical imaging, computer hardware, and machine-learning algorithms have resulted in the increased use of these tools in the field of medicine as a whole and specifically in cancer imaging for detection and characterization of malignant lesions, prognosis, and assessment of treatment response. Among the currently available imaging techniques, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an important role in the evaluation of treatment assessment of many cancers, given its superior soft-tissue contrast and its ability to allow multiplanar imaging and functional evaluation. In recent years, deep learning (DL) has become an active area of research, paving the way for computer-assisted clinical and radiological decision support. DL can uncover associations between imaging features that cannot be visually identified by the naked eye and pertinent clinical outcomes. The aim of this review is to highlight the use of DL in the evaluation of tumor response assessed on MRI. In this review, we will first provide an overview of common DL architectures used in medical imaging research in general. Then, we will review the studies to date that have applied DL to magnetic resonance imaging for the task of treatment response assessment. Finally, we will discuss the challenges and opportunities of using DL within the clinical workflow.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep computational pathology in breast cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Jul;72:226-237. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.08.006. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 32818626 Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Breast cancer detection using deep learning: Datasets, methods, and challenges ahead.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Oct;149:106073. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106073. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36103745 Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of myocardial viability: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(15):1-45. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074392 Free PMC article.
-
AAPM task group report 273: Recommendations on best practices for AI and machine learning for computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging.Med Phys. 2023 Feb;50(2):e1-e24. doi: 10.1002/mp.16188. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36565447
Cited by
-
Future AI Will Most Likely Predict Antibody-Drug Conjugate Response in Oncology: A Review and Expert Opinion.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 5;16(17):3089. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173089. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. . New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. european organization for research and treatment of cancer, national cancer institute of the united states, national cancer institute of canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000; 92: 205–16. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.3.205 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi H, Charnsangavej C, Faria SC, Macapinlac HA, Burgess MA, Patel SR, et al. . Correlation of computed tomography and positron emission tomography in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated at a single institution with imatinib mesylate: proposal of new computed tomography response criteria. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1753–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.3049 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

