HPV-Induced MiR-21 Promotes Epithelial Mesenchymal Transformation and Tumor Progression in Cervical Cancer Cells through the TGF β R2/hTERC Pathway
- PMID: 36105448
- PMCID: PMC9458404
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6297694
HPV-Induced MiR-21 Promotes Epithelial Mesenchymal Transformation and Tumor Progression in Cervical Cancer Cells through the TGF β R2/hTERC Pathway
Abstract
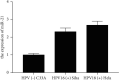
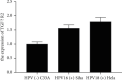
Cervical cancer (CC) is a common malignant tumor in women. It ranks first among the malignant tumors of woman reproductive organs and is one of the most important cancers in the world. Current studies suggest that human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially high-risk persistent infection, is the basic cause of cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) plays a role similar to oncogenes in the occurrence and growth of malignant tumors and can be developed as a potential target for treating malignant tumors. Recently, the study of the mechanism of malignant invasion and metastasis has made great progress. The current consensus is that the invasion and metastasis of malignant tumors is a complicated biological process with multistep and multigene control; the process of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) may be the initial event of invasion and metastasis of epithelial malignant tumors. EMT means that epithelial cells obtain the characteristics of mesenchymal cells, which has main characteristics such as the loss of epithelial cell characteristics and the achievement of mesenchymal cell features, and then induce epithelial cells to acquire the ability of migration and invasion, and participate in many physiological and pathological processes of human body, including embryogenesis, organ differentiation, tissue inflammation, and wound healing. Research has proved that miR-21 is associated with the invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer, and its specific mechanism has not been completely clear; EMT exerts a significant effect on the invasion and metastasis of epithelial malignant tumors; we speculate whether miR-21 regulates the EMT process of cervical cancer cells. ELISA and RT-PCR studied HPV-induced cervical cancer cells, and it was found that HPV may induce miR-21 to pass through the TGF β R2/hTERC pathway which promotes epithelial stromal transformation and tumor progression of cervical cancer cells.
Copyright © 2022 Ying Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-218 inhibits EMT, migration and invasion by targeting SFMBT1 and DCUN1D1 in cervical cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45622-45636. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9850. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27285984 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1/microRNA-202-3p/periostin axis modulates invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human cervical cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):14170-14180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28113. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30633360
-
LncRNA-CTS promotes metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulating miR-505/ZEB2 axis in cervical cancer.Cancer Lett. 2019 Nov 28;465:105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31499118
-
Infection by High-Risk Human Papillomaviruses, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Squamous Pre-Malignant or Malignant Lesions of the Uterine Cervix: A Series of Chained Events?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13543. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413543. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insight in urological cancer therapy: From epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to application of nano-biomaterials.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 15;229:115672. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115672. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36906272 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation and analysis of female HPV infection and genotype distribution in Xuhui District, Shanghai.Virol J. 2025 Mar 5;22(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02663-4. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40045415 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interaction of human papilloma virus (HPV) with microRANs: insights into the development of cervical cancer and treatment approaches.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Jul 23;20(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00677-9. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40702513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organoid technology in cervical cancer research.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 May 15;15(5):1988-2003. doi: 10.62347/FNTD1712. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40520874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Papillomavirus-Encoded microRNAs as Regulators of Human Gene Expression in Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Transcriptomics Study.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Jun 9;11(3):43. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11030043. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40559621 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Human Papillomavirus on microRNA-21 Expression in Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 23;25(15):8038. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158038. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125608 Free PMC article.