Disposable paper-based microfluidics for fertility testing
- PMID: 36105592
- PMCID: PMC9465368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104986
Disposable paper-based microfluidics for fertility testing
Abstract
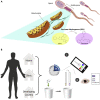
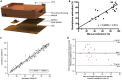
Fifteen percent of couples of reproductive age suffer from infertility globally and the burden of infertility disproportionately impacts residents of developing countries. Assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs), including in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), have been successful in overcoming various reasons for infertility including borderline and severe male factor infertility which consists of 20%-30% of all infertile cases. Approximately half of male infertility cases stem from suboptimal sperm parameters. Therefore, healthy/normal sperm enrichment and sorting remains crucial in advancing reproductive medicine. Microfluidic technologies have emerged as promising tools to develop in-home rapid fertility tests and point-of-care (POC) diagnostic tools. Here, we review advancements in fabrication methods for paper-based microfluidic devices and their emerging fertility testing applications assessing sperm concentration, sperm motility, sperm DNA analysis, and other sperm functionalities, and provide a glimpse into future directions for paper-based fertility microfluidic systems.
Keywords: Biodevices; Biotechnology; Medical device in health technology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S.T. is a co-founder of and has equity interest in GetDeHealth, a company that is developing microfluidic technologies for point-of-care diagnostic and wellness solutions. The interests of S.T. were viewed and managed in accordance with the conflict of interest policies. Author S.T. is a member of the iScience Editorial Board. B.A. is a member of ART Fertility Clinics, a company working on human reproductive medicine. The interests of B.A. were viewed and managed in accordance with the conflict of interest policies. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures




References
-
- Abe K., Suzuki K., Citterio D. Inkjet-printed microfluidic multianalyte chemical sensing paper. Anal. Chem. 2008;80:6928–6934. - PubMed
-
- Abe K., Kotera K., Suzuki K., Citterio D. Inkjet-printed paperfluidic immuno-chemical sensing device. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010;398:885–893. - PubMed
-
- Amin R., Ghaderinezhad F., Li L., Lepowsky E., Yenilmez B., Knowlton S., Tasoglu S. Continuous-ink, multiplexed pen-plotter approach for low-cost, high-throughput fabrication of paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2017;89:6351–6357. - PubMed
-
- Amin R., Knowlton S., Yenilmez B., Hart A., Joshi A., Tasoglu S. Smart-phone attachable, flow-assisted magnetic focusing device. RSC Adv. 2016;6:93922–93931.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

