A novel immersive virtual reality environment for the motor rehabilitation of stroke patients: A feasibility study
- PMID: 36105763
- PMCID: PMC9465047
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2022.906424
A novel immersive virtual reality environment for the motor rehabilitation of stroke patients: A feasibility study
Abstract
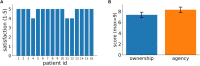
We designed and implemented an immersive virtual reality (VR) environment for upper limb rehabilitation, which possesses several notable features. First, by exploiting modern computer graphics its can present a variety of scenarios that make the rehabilitation routines challenging yet enjoyable for patients, thus enhancing their adherence to the therapy. Second, immersion in a virtual 3D space allows the patients to execute tasks that are closely related to everyday gestures, thus enhancing the transfer of the acquired motor skills to real-life routines. Third, in addition to the VR environment, we also developed a client app running on a PC that allows to monitor in real-time and remotely the patients' routines thus paving the way for telerehabilitation scenarios. Here, we report the results of a feasibility study in a cohort of 16 stroke patients. All our patients showed a high degree of comfort in our immersive VR system and they reported very high scores of ownership and agency in embodiment and satisfaction questionnaires. Furthermore, and notably, we found that behavioral performances in our VR tasks correlated with the patients' clinical scores (Fugl-Meyer scale) and they could thus be used to assess improvements during the rehabilitation program. While further studies are needed, our results clearly support the feasibility and effectiveness of VR-based motor rehabilitation processes.
Keywords: fugl-meyer; head-mount display; immersive virtual reality; motor rehabilitation; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Fregna, Schincaglia, Baroni, Straudi and Casile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of Immersive Virtual Reality on Upper-Extremity Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 27;13(1):146. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010146. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38202153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the effect and mechanism of upper limb motor function recovery induced by immersive virtual-reality-based rehabilitation for subacute stroke subjects: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Feb 6;20(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3177-y. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30728055 Free PMC article.
-
Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Using Fully Immersive Virtual Reality Games With a Head Mount Display: A Feasibility Study.PM R. 2020 Mar;12(3):257-262. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.12206. Epub 2019 Sep 3. PM R. 2020. PMID: 31218794
-
The Role of Immersive Virtual Reality in Upper Limb Rehabilitation for Subacute Stroke: A Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 12;14(6):1903. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061903. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness, safety and patients' perceptions of an immersive virtual reality-based exercise system for poststroke upper limb motor rehabilitation: A proof-of-concept and feasibility randomized controlled trial.Digit Health. 2023 Sep 26;9:20552076231203599. doi: 10.1177/20552076231203599. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37766909 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Design of Virtual Reality Exergames for Upper Limb Stroke Rehabilitation Following Iterative Design Methods: Usability Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 Jan 11;12:e48900. doi: 10.2196/48900. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 38206670 Free PMC article.
-
Immersive Virtual Reality in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Its Efficacy in Upper Limb Recovery.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 7;14(6):1783. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061783. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A quantitative assessment of the hand kinematic features estimated by the oculus Quest 2.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;15(1):8842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91552-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087370 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a Virtual Reality rehabilitation in stroke patients with sensory-motor and proprioception upper limb deficit: A study protocol.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 12;19(8):e0307408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307408. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39133660 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Immersive Virtual Reality on Physical Function, Fall-Related Outcomes, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 24;13(15):1800. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13151800. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blascovich J., Loomis J., Beall A. C., Swinth K. R., Hoyt C. L., Bailenson J. N. (2002). Target article: Immersive virtual environment technology as a methodological tool for social psychology. Psychol. Inq. 13 (2), 103–124. 10.1207/S15327965PLI1302_01 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

