The role of gut microbiome in immune modulation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36105887
- PMCID: PMC9465582
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359221122714
The role of gut microbiome in immune modulation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
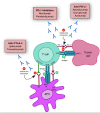
Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinomas (mRCC) has drastically improved since the advent of immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), with a significant proportion of patients achieving durable responses. While this has revolutionized treatment and improved outcomes for mRCC patients, a large subset of patients still does not respond to treatment with ICIs. Moreover, ICIs can induce various immune-related adverse events, limiting their use in many patients. Therefore, there is a need to identify the predictive biomarkers of both efficacy and toxicity associated with ICIs, which would allow for a more personalized approach and help with clinical decision-making. This review aims to explore the role of the gut microbiome in RCC to overcome primary resistance and predict response to treatment with ICIs. First, current therapeutic strategies and mechanisms of action of ICI therapies for RCC treatment will be reviewed. With the technological development of shotgun whole-genome sequencing, the gut microbiome has emerged as an exciting field of research within oncology. Thus, the role of the microbiome and its bidirectional interaction with ICIs and other drugs will be explored, with a particular focus on the microbiome profile in RCC. Lastly, the rationale for future clinical interventions to overcome resistance to ICIs using fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with RCC will be presented.
Keywords: immunotherapy; microbiome; predictive biomarker; renal cell carcinoma; tumor microenvironment.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RF has the following disclosures: Advisory Board or Honoraria: Merck, Novartis, Ipsen, Janssen, Pfizer, BMS, Bayer; Travel Grant: Janssen. The other authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging resistance vs. losing response to immune check point inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma: two differing phenomena.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Sep 20;6(3):642-655. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.47. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37842239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Biomarkers of Response and Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 12;15(12):3159. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123159. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota and immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 15;19(3):2268982. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2268982. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37955340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut and urinary microbiota: the causes and potential treatment measures of renal cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 27;14:1188520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188520. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37441065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Gut Microbiome and Cancer Immunotherapy: Can We Use the Gut Microbiome as a Predictive Biomarker for Clinical Response in Cancer Immunotherapy?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 27;13(19):4824. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194824. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complete Response in Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: Remission or Healing? How to Improve Patients' Outcomes?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;15(3):793. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030793. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Promising Biomarkers and the Challenges to Reach the Clinic.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 16;30(4):663-672. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1892. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 37874628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota, Metabolic Disorders and Breast Cancer: Could Berberine Turn Out to Be a Transversal Nutraceutical Tool? A Narrative Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 19;23(20):12538. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012538. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293390 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological adverse events associated with PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 29;17:1227049. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1227049. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37456998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically predicted inflammatory proteins mediate the association between gut microbiota and renal cell carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 20;16(1):216. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01980-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39976778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Tomczak P, Park SH, et al.. Adjuvant pembrolizumab after nephrectomy in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2021; 385: 683–694. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al.. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015; 136: E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Heng DYC, Xie W, Regan MM, et al.. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5794–5799. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

