Cost-effectiveness analysis of personalised versus standard dosimetry for selective internal radiation therapy with TheraSphere in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36106105
- PMCID: PMC9464985
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.920073
Cost-effectiveness analysis of personalised versus standard dosimetry for selective internal radiation therapy with TheraSphere in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aims: To perform a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) comparing personalised dosimetry with standard dosimetry in the context of selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) with TheraSphere for the management of adult patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the Italian Healthcare Service perspective.
Materials and methods: A partition survival model was developed to project costs and the quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) over a lifetime horizon. Clinical inputs were retrieved from a published randomised controlled trial. Health resource utilisation inputs were extracted from the questionnaires administered to clinicians in three oncology centres in Italy, respectively. Cost parameters were based on Italian official tariffs.
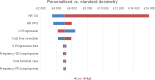
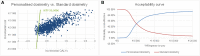
Results: Over a lifetime horizon, the model estimated the average QALYs of 1.292 and 0.578, respectively, for patients undergoing personalised and standard dosimetry approaches. The estimated mean costs per patient were €23,487 and €19,877, respectively. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) of personalised versus standard dosimetry approaches was €5,056/QALY.
Conclusions: Personalised dosimetry may be considered a cost-effective option compared to standard dosimetry for patients undergoing SIRT for HCC in Italy. These findings provide evidence for clinicians and payers on the value of personalised dosimetry as a treatment option for patients with HCC.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness; cost-utility; personalised dosimetry; tailored treatment; trans-arterial radioembolisation.
Copyright © 2022 Rognoni, Barcellona, Bargellini, Bavetta, Bellò, Brunetto, Carucci, Cioni, Crocetti, D’Amato, D’Amico, Deagostini, Deandreis, De Simone, Doriguzzi, Finessi, Fonio, Grimaldi, Ialuna, Lagattuta, Masi, Moreci, Scalisi, Virdone and Tarricone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study received funding from Confindustria Dispositivi Medici Servizi Srl. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures

References
-
- Worldwide cancer data. (2022) London: World Cancer Research Fund International. Available at: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/worldwide-cancer-data/.
-
- Hepatocellular carcinoma: Considerations for managed care professionals. Available at: https://www.ajmc.com/view/hepatocellular-carcinoma-considerations-for-ma.... - PubMed
-
- Dawson LA, McGinn CJ, Normolle D, Ten Haken RK, Walker S, Ensminger W, et al. . Escalated focal liver radiation and concurrent hepatic artery fluorodeoxyuridine for unresectable intrahepatic malignancies. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol (2000) 18(11):2210–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.11.2210 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

