DCE-MRI radiomics models predicting the expression of radioresistant-related factors of LRP-1 and survivin in locally advanced rectal cancer
- PMID: 36106114
- PMCID: PMC9465298
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.881341
DCE-MRI radiomics models predicting the expression of radioresistant-related factors of LRP-1 and survivin in locally advanced rectal cancer
Abstract
Objective: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1) and survivin are associated with radiotherapy resistance in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). This study aimed to evaluate the value of a radiomics model based on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) for the preoperative assessment of LRP-1 and survivin expressions in these patients.
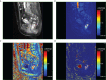
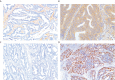
Methods: One hundred patients with pathologically confirmed LARC who underwent DCE-MRI before surgery between February 2017 and September 2021 were included in this retrospective study. DCE-MRI perfusion histogram parameters were calculated for the entire lesion using post-processing software (Omni Kinetics, G.E. Healthcare, China), with three quantitative parameter maps. LRP-1 and survivin expressions were assessed by immunohistochemical methods and patients were classified into low- and high-expression groups.
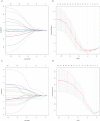
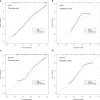
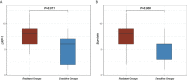
Results: Four radiomics features were selected to construct the LRP-1 discrimination model. The LRP-1 predictive model achieved excellent diagnostic performance, with areas under the receiver operating curve (AUCs) of 0.853 and 0.747 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. The other four radiomics characteristics were screened to construct the survivin predictive model, with AUCs of 0.780 and 0.800 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Decision curve analysis confirmed the clinical usefulness of the radiomics models.
Conclusion: DCE-MRI radiomics models are particularly useful for evaluating LRP-1 and survivin expressions in patients with LARC. Our model has significant potential for the preoperative identification of patients with radiotherapy resistance and can serve as an essential reference for treatment planning.
Keywords: LRP-1; dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI); locally advanced rectal cancer; radiomics models; survivin.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Huang, Wang, Zhao, Ma, Wang, Mao, Liu, Yang, Pan and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preoperative Prediction of Extramural Venous Invasion in Rectal Cancer: Comparison of the Diagnostic Efficacy of Radiomics Models and Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 9;10:459. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00459. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32328461 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-modal radiomics model to predict treatment response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 21;26(19):2388-2402. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2388. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32476800 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-parameter diffusion and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging and radiomics nomogram for preoperative evaluation of aquaporin-1 expression in rectal cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022 Apr;47(4):1276-1290. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03397-x. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35166938
-
Radiomics analysis of multiparametric MRI for prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.Eur Radiol. 2019 Mar;29(3):1211-1220. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5683-9. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30128616
-
Radiomics Based on Multimodal MRI for the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Aug;52(2):596-607. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27098. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32061014
Cited by
-
Diagnostic performance of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parameters and serum tumor markers in rectal carcinoma prognosis.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 May 15;16(5):1796-1807. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1796. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38764818 Free PMC article.
-
Radiogenomics: Contemporary Applications in the Management of Rectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 12;15(24):5816. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245816. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CT-based radiomics predicts CD38 expression and indirectly reflects clinical prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 13;10(12):e32910. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32910. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38948050 Free PMC article.
-
The Co-Delivery of Natural Products and Small RNAs for Cancer Therapy: A Review.Molecules. 2025 Mar 27;30(7):1495. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071495. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between radiomics features of DCE-MRI and CD8+ and CD4+ TILs in advanced gastric cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Jun 5;29:1611001. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1611001. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37342362 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

