The modulatory action of C-Vx substance on the immune system in COVID-19
- PMID: 36106521
- PMCID: PMC9639513
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2125347
The modulatory action of C-Vx substance on the immune system in COVID-19
Abstract
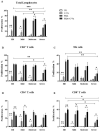
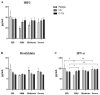
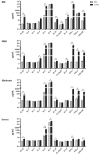
The modulatory effect of C-Vx, a novel therapeutic agent, on the immune system of COVID-19 patients was investigated. The functions of T and NK cells of COVID-19 patients with different disease severity were evaluated by flow cytometry in response to C-Vx stimulation. The levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were detected by multiplex assay in supernatants after cell culture with C-Vx. Bradykinin, IRF3, and IFN-α levels were also measured by ELISA in the presence or absence of C-Vx stimulation. As a result, increased CD107a expression was observed on NK cells in response to C-Vx addition. The proliferation of T cell subsets was increased by C-Vx, decreasing by disease severity. IL-4 and IL-10 levels were elevated while IFN-γ and IL-17 levels were reduced in T cells following C-Vx stimulation. However, the levels of pro-inflammatory IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IFN-γ and GM-CSF were significantly increased upon C-Vx stimulation. IFN-α levels tended to increase after incubation with C-Vx. These findings support an immunomodulatory action of C-Vx on the immune system of patients with a mild and moderate phase of COVID-19.
Keywords: C-Vx; COVID-19; cytokines; cytotoxicity; immune system; inflammation; lymphocytes; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, et al. . Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(5):503–510. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
