ONSET-1 Phase 2b Randomized Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of OC-01 (Varenicline Solution) Nasal Spray on Signs and Symptoms of Dry Eye Disease
- PMID: 36107843
- PMCID: PMC9473713
- DOI: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002941
ONSET-1 Phase 2b Randomized Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of OC-01 (Varenicline Solution) Nasal Spray on Signs and Symptoms of Dry Eye Disease
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this trial was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of OC-01 (varenicline solution), a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist nasal spray, on signs and symptoms of dry eye disease.
Methods: A phase 2b, multicenter, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled trial (ONSET-1; NCT03636061) was performed. Patients were aged 22 years or older with a physician's diagnosis of dry eye disease and previous use of artificial tears were randomized 1:1:1:1 to control (vehicle nasal spray twice daily [BID]), OC-01 0.006 mg BID, OC-01 0.03 mg BID, and OC-01 0.06 mg BID. The primary end point was the change in the anesthetized Schirmer test score from baseline to day 28 in the study eye. The secondary end points included the change in the eye dryness score from baseline to day 28.
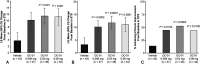
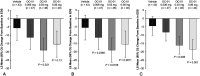
Results: One hundred eighty-two patients were randomized. After 28 days, patients who received OC-01 0.03 or 0.06 mg showed a statistically significant improvement in tear film production relative to vehicle, with least squares mean differences from vehicle of 7.7 mm [95% confidence interval, 3.8-11.7; P < 0.001] with OC-01 0.03 mg and 7.5 mm (95% confidence interval, 3.4-11.6; P < 0.001) with OC-01 0.06 mg. Patients receiving OC-01 0.03 mg showed a significant reduction in the eye dryness score by day 28 versus vehicle (P = 0.021); those receiving the OC-01 0.06 mg dose showed a nonsignificant reduction versus vehicle. OC-01 administration was associated with sneezing (62%-84%) and cough (9%-25%); these were transient and predominantly mild in severity.
Conclusions: OC-01 nasal spray administered BID at 0.03 and 0.06 mg resulted in significant improvements in signs and symptoms of dry eye disease, was well tolerated, and warrants further clinical investigation.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Wirta and G. L. Torkildsen have received research grant support from Oyster Point Pharma, Inc. D. A. Hollander is an employee of Ora, Inc. E. Bendert was an employee at Statistics Collaborative, Inc at the time the study was conducted. L. Zeng is a current employee at Statistics Collaborative, Inc. M. Ackermann is a board member at Oyster Point Pharma, Inc. J. Nau is an employee at and shareholder of Oyster Point Pharma, Inc. The remaining author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

