Stop and think: Additional time supports monitoring processes in young children
- PMID: 36107922
- PMCID: PMC9477363
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274460
Stop and think: Additional time supports monitoring processes in young children
Abstract
When children evaluate their certainty, monitoring is often inaccurate. Even though young children struggle to estimate their confidence, existing research shows that monitoring skills are developing earlier than expected. Using a paired associates learning task with integrated monitoring, we implemented a time window to-"Stop and Think"-before children generated their answers and evaluated their confidence in the chosen response. Results show that kindergarten and second grade children in the-"Stop and Think"-condition have higher monitoring accuracy than the control group. Implementing a time window thus seems to support children in their evaluation of different certainty levels. Relating individual differences in independently measured inhibitory control skills revealed a correlation between monitoring and inhibition for kindergarteners.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
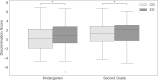
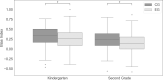
References
-
- Schneider W, Löffler E. The development of metacognitive knowledge in children and adolescents. In Dunlosky J. & Tauber S. K. (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of metamemory. 2015; 491–518. Oxford University Press. 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199336746.013.10 - DOI
-
- Flavell JH. Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry. American Psychologist. 1979; 34(10):906–911. 10.1037/0003-066x.34.10.906 - DOI

