High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation modulates theta response during a Go-NoGo task in traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 36108520
- PMCID: PMC10545365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2022.08.015
High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation modulates theta response during a Go-NoGo task in traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Objective: High Definition transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (HD-tDCS) has been shown to improve cognitive performance in individuals with chronic traumatic brain injury (TBI), although electrophysiological mechanisms remain unclear.
Methods: Veterans with TBI underwent active anodal (N = 15) vs sham (N = 10) HD-tDCS targeting the pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA). A Go-NoGo task was conducted simultaneously with electroencephalography (EEG) at baseline and after intervention completion.
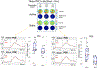
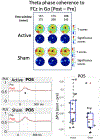
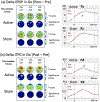
Results: We found increased theta event-related spectral perturbation (ERSP) and inter-trial phase coherence (ITPC) during Go in the frontal midline electrodes overlying the pre-SMA after active HD-tDCS intervention, but not after sham. We also found increased theta phase coherence during Go between the frontal midline and left posterior regions after active HD-tDCS. A late increase in alpha-theta ERSP was found in the left central region after active HD-tDCS. Notably, lower baseline theta ERSP/ITPC in the frontal midline region predicted more post-intervention improvement in Go performance only in the active group.
Conclusions: There are local and interregional oscillatory changes in response to HD-tDCS modulation in chronic TBI.
Significance: These findings may guide future research in utilizing EEG time-frequency metrics not only to measure interventional effects, but also in selecting candidates who may optimally respond to treatment.
Keywords: EEG; Electromodulation; Go-NoGo; HD-tDCS; Pre-SMA; TBI; Veterans; tDCS.
Copyright © 2022 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships relevant to the work.
Figures
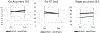
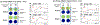

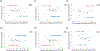
References
-
- Benton LA, Hamsher K, and Sivan AB (1994). Multilingual Aphasia Examination. AJA Associates: Iowa City, IA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

