Directing the Way-Receptor and Chemical Targeting Strategies for Nucleic Acid Delivery
- PMID: 36109461
- PMCID: PMC9483255
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-022-03385-w
Directing the Way-Receptor and Chemical Targeting Strategies for Nucleic Acid Delivery
Abstract
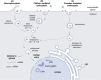
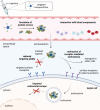
Nucleic acid therapeutics have shown great potential for the treatment of numerous diseases, such as genetic disorders, cancer and infections. Moreover, they have been successfully used as vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic. In order to unfold full therapeutical potential, these nano agents have to overcome several barriers. Therefore, directed transport to specific tissues and cell types remains a central challenge to receive carrier systems with enhanced efficiency and desired biodistribution profiles. Active targeting strategies include receptor-targeting, mediating cellular uptake based on ligand-receptor interactions, and chemical targeting, enabling cell-specific delivery as a consequence of chemically and structurally modified carriers. With a focus on synthetic delivery systems including polyplexes, lipid-based systems such as lipoplexes and lipid nanoparticles, and direct conjugates optimized for various types of nucleic acids (DNA, mRNA, siRNA, miRNA, oligonucleotides), we highlight recent achievements, exemplified by several nucleic acid drugs on the market, and discuss challenges for targeted delivery to different organs such as brain, eye, liver, lung, spleen and muscle in vivo.
Keywords: lipoplex; pDNA; polyplex; siRNA; targeting.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Worldwide. 09.05.2022. Available from: https://a873679.fmphost.com/fmi/webd/GTCT.
-
- Mulligan RC. The basic science of gene therapy. Science. 1993;260(5110):926–932. - PubMed
-
- Friedmann T, Roblin R. Gene therapy for human genetic disease? Science. 1972;175(4025):949–955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

