Association of inflammatory and angiogenic biomarkers in maternal plasma with retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants
- PMID: 36109603
- PMCID: PMC10275990
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-022-02234-9
Association of inflammatory and angiogenic biomarkers in maternal plasma with retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether various novel inflammatory and angiogenic biomarkers in maternal plasma, alone or in combination with baseline antenatal factors, could predict retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) in preterm infants.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on 140 premature singleton neonates born to women with preterm birth (≤32 weeks) and screened for ROP. Maternal blood obtained at the time of admission was assayed for CRP, endoglin, endostatin, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, IL-6, LBP, MMP-8, PlGF, S100A8/A9, TGFBI, and VEGFR-1. The primary outcome measures included severe ROP (stage 3 or higher) and type 1 ROP requiring treatment.
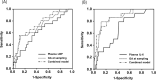
Results: ROP was present in 25.7% (36/140) of the study population, including 20 (14.3%) cases of severe ROP and 14 (10%) with type 1 ROP. Multiple logistic regression analyses revealed significant associations between high concentrations of maternal plasma LBP and severe ROP, and between elevated plasma IL-6 and LBP levels and type 1 ROP (all P < 0.05), while adjusting for confounders (i.e., gestational age [GA] at sampling). Prenatal prediction models for severe ROP and type 1 ROP were developed by combining plasma IL-6 or LBP levels with GA at sampling, which showed good discriminatory power (area under the curve = 0.747 and 0.854, respectively).
Conclusions: IL-6 and LBP in maternal plasma were found to be independently associated with severe ROP and type 1 ROP. Prediction models based on these biomarkers along with GA at sampling may serve as good prenatal indicators for the neonatal risk of ROP progression in women at risk of preterm birth.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Royal College of Ophthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cord blood transforming growth factor-β-induced as predictive biomarker of retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Sep;261(9):2477-2488. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06056-7. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37022494
-
Histological Chorioamnionitis and Funisitis as New Risk Factors for Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Meta-analysis.Am J Perinatol. 2024 May;41(S 01):e3264-e3273. doi: 10.1055/a-2215-0662. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Am J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 37989252 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory and Angiogenic Mediators in Amniotic Fluid Are Associated With the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Infants.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 May 11;61(5):42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.42. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32446247 Free PMC article.
-
Immune and Inflammatory Proteins in Cord Blood as Predictive Biomarkers of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Infants.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Sep 3;60(12):3813-3820. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-27258. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31525777
-
Demographic Risk Factors of Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies.Neonatology. 2022;119(2):151-163. doi: 10.1159/000519635. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Neonatology. 2022. PMID: 35124682
Cited by
-
Targeted dexamethasone nano-prodrug for corneal neovascularization management.Biomed J. 2024 Feb;47(1):100592. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.03.005. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37004870 Free PMC article.
-
Cord blood transforming growth factor-β-induced as predictive biomarker of retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Sep;261(9):2477-2488. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06056-7. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37022494
-
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP): An Overview of Biomarkers in Various Samples for Prediction, Diagnosis, and Prognosis.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 May 7;19:1515-1530. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S519292. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40357456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Cytokines in Retinopathy of Prematurity.J Pers Med. 2023 Feb 5;13(2):291. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020291. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histological Chorioamnionitis and Funisitis as New Risk Factors for Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Meta-analysis.Am J Perinatol. 2024 May;41(S 01):e3264-e3273. doi: 10.1055/a-2215-0662. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Am J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 37989252 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

