CCL7 as a novel inflammatory mediator in cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease
- PMID: 36109744
- PMCID: PMC9479413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-022-01626-1
CCL7 as a novel inflammatory mediator in cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease
Abstract
Chemokines are key components in the pathology of chronic diseases. Chemokine CC motif ligand 7 (CCL7) is believed to be associated with cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease. CCL7 may play a role in inflammatory events by attracting macrophages and monocytes to further amplify inflammatory processes and contribute to disease progression. However, CCL7-specific pathological signaling pathways need to be further confirmed in these chronic diseases. Given the multiple redundancy system among chemokines and their receptors, further experimental and clinical studies are needed to clarify whether direct CCL7 inhibition mechanisms could be a promising therapeutic approach to attenuating the development of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Chemokine; Chemokine CC motif ligand 7; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic kidney disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
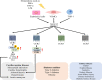
Figures
References
-
- Ardigo D, Assimes TL, Fortmann SP, Go AS, Hlatky M, Hytopoulos E, Iribarren C, Tsao PS, Tabibiazar R, Quertermous T. Circulating chemokines accurately identify individuals with clinically significant atherosclerotic heart disease. Physiol Genomics. 2007;31(3):402–409. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00104.2007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

