Repositioning of drugs for Parkinson's disease and pharmaceutical nanotechnology tools for their optimization
- PMID: 36109747
- PMCID: PMC9479294
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01612-5
Repositioning of drugs for Parkinson's disease and pharmaceutical nanotechnology tools for their optimization
Abstract
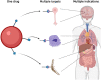
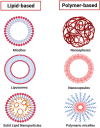
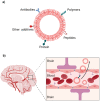
Parkinson's disease (PD) significantly affects patients' quality of life and represents a high economic burden for health systems. Given the lack of safe and effective treatments for PD, drug repositioning seeks to offer new medication alternatives, reducing research time and costs compared to the traditional drug development strategy. This review aimed to collect evidence of drugs proposed as candidates to be reused in PD and identify those with the potential to be reformulated into nanocarriers to optimize future repositioning trials. We conducted a detailed search in PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus from January 2015 at the end of 2021, with the descriptors "Parkinson's disease" and "drug repositioning" or "drug repurposing". We identified 28 drugs as potential candidates, and six of them were found in repositioning clinical trials for PD. However, a limitation of many of these drugs to achieve therapeutic success is their inability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), as is the case with nilotinib, which has shown promising outcomes in clinical trials. We suggest reformulating these drugs in biodegradable nanoparticles (NPs) based on lipids and polymers to perform future trials. As a complementary strategy, we propose functionalizing the NPs surface by adding materials to the surface layer. Among other advantages, functionalization can promote efficient crossing through the BBB and improve the affinity of NPs towards certain brain regions. The main parameters to consider for the design of NPs targeting the central nervous system are highlighted, such as size, PDI, morphology, drug load, and Z potential. Finally, current advances in the use of NPs for Parkinson's disease are cited.
Keywords: Drug repositioning; Drug repurposing; Nanocarriers; Nanoparticles; Parkinson’s disease; Pharmaceutical nanotechnology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drug repositioning for Parkinson's disease: An emphasis on artificial intelligence approaches.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102651. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102651. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39755176 Review.
-
Does drug repurposing bridge the gaps in management of Parkinson's disease? Unravelling the facts and fallacies.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Mar;105:102693. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102693. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39961372 Review.
-
Drug Repurposing in Parkinson's Disease.CNS Drugs. 2018 Aug;32(8):747-761. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0548-y. CNS Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30066310 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Drug Repurposing for Parkinson's Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(28):5340-5362. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180719144850. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30027839 Review.
-
A bidirectional drug repositioning approach for Parkinson's disease through network-based inference.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Feb 13;457(3):280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.101. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25576361
Cited by
-
Drug repurposing for Parkinson's disease by biological pathway based edge-weighted network proximity analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 11;14(1):21258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71922-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39261542 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving Landscape of Parkinson's Disease Research: Challenges and Perspectives.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 8;10(2):1864-1892. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09114. eCollection 2025 Jan 21. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39866628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold Nanoparticles in Parkinson's Disease Therapy: A Focus on Plant-Based Green Synthesis.Cureus. 2024 Feb 22;16(2):e54671. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54671. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38524031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Repurposing.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2411325. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411325. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40047357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying potential repurposable medications for Parkinson's disease through Mendelian randomization analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 24;14(1):19670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70758-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39181920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saavedra Moreno JS, Millán PA, Buriticá Henao OF. Introducción, epidemiología y diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Parkinson. Acta Neurol Colomb. 2019;35(1):2–10. doi: 10.22379/24224022244. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

