Synthesis, biological evaluation and in-silico ADME studies of novel series of thiazolidin-2,4-dione derivatives as antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer agents
- PMID: 36109764
- PMCID: PMC9479363
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-022-00861-7
Synthesis, biological evaluation and in-silico ADME studies of novel series of thiazolidin-2,4-dione derivatives as antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer agents
Abstract
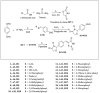
Background: A novel series of thiazolidine-2,4-dione molecules was derived and their chemical structures were established using physiochemical parameters and spectral techniques (1H-NMR, IR, MS etc.). The synthesized molecule were then evaluated for their antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial potential.
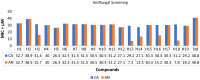
Results and discussion: Serial tube dilution method was employed to evaluate the antimicrobial potential against selected fungal and bacterial strains by taking fluconazole and cefadroxil as reference antifungal and antibacterial drugs respectively. 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging activity was used to assess the antioxidant potential of the synthesized analogues. Further, the anticancer potential of the selected molecules was assessed against DU-145 cancer cell lines using MTT assay. The drug-likeness was also evaluated by studying in-silico ADME parameters of the synthesized analogues.
Conclusion: In antioxidant evaluation studies, the analogue H5 with IC50 = 14.85 μg/mL was found to be the most active molecule. The antimicrobial evaluation outcomes suggested that the molecules H5, H13, H15 and H18 possessed moderate to promising activity against the selected species of microbial strains having MIC range 7.3 µM to 26.3 µM. The results of anticancer evaluation revealed that all the screened derivatives possess mild anticancer potential. The in-silico ADME studies revealed that all the compounds were found to be drug-like.
Keywords: ADME; Anticancer; Antimicrobial; Antioxidant; Characterization; Synthesis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declares that they have no competing interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, in silico studies and biological evaluation of 5-((E)-4-((E)-(substituted aryl/alkyl)methyl)benzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives.BMC Chem. 2020 Mar 31;14(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13065-020-00678-2. eCollection 2020 Dec. BMC Chem. 2020. PMID: 32266332 Free PMC article.
-
2-Substituted-3-(5-Substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol/thiadiazol-2-yl) Thiazolidin-4-one Derivatives: Synthesis, Anticancer, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Potential.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 29;16(6):805. doi: 10.3390/ph16060805. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375752 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico studies of some new analogues of 3,5-vdisubstituted thiazolidin-2,4-dione.Future Med Chem. 2023 Dec;15(24):2257-2268. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2023-0237. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Future Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37982252
-
Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potency of NSubstituted- 2-Sulfanylidene-1,3-Thiazolidin-4-one Derivatives and QSAR Study.Med Chem. 2019;15(8):840-849. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666181205163052. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30520381
-
Chemical Synthesis, Mechanism of Action and Anticancer Potential of Medicinally Important Thiazolidin-2,4-dione Derivatives: A Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019;19(18):1474-1516. doi: 10.2174/1389557519666190513093618. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31092179 Review.
Cited by
-
Medicinal Perspective of 2,4-Thiazolidinediones Derivatives: An Insight into Recent Advancements.ChemistryOpen. 2024 Nov;13(11):e202400147. doi: 10.1002/open.202400147. Epub 2024 Sep 9. ChemistryOpen. 2024. PMID: 39246226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multitarget Pharmacology of Sulfur-Nitrogen Heterocycles: Anticancer and Antioxidant Perspectives.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 25;13(8):898. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080898. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and mechanistic anticancer activity of new acetylated 5-aminosalicylate-thiazolinone hybrid derivatives.iScience. 2023 Dec 9;27(1):108659. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108659. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38235331 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer and Antioxidant Properties of Vernonia amygdalina Delile and Citrus aurantifolia (Christm.) Swingle Juice Extracts: An In Vitro Study.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Oct 30;2024:9692656. doi: 10.1155/2024/9692656. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39512596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althagafi I, Farghaly TA, Abbas EMH, Harras MF. Benzosuberone as precursor for synthesis of antimicrobial agents: synthesis, antimicrobial activity, and molecular docking. Polycycl Aromat Compd. 2021;41(8):1646–1666. doi: 10.1080/10406638.2019.1692877. - DOI
-
- Kumar H, Kumar P, Narasimhan B, Ramasamy K, Mani V, Mishra RK, et al. Synthesis, in vitro antimicrobial, antiproliferative, and QSAR studies of N-(substituted phenyl)-2/4-(1H-indol-3-ylazo)-benzamides. Med Chem Res. 2013;22:1957–1971. doi: 10.1007/s00044-012-0181-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
