Genetic regulation of RNA splicing in human pancreatic islets
- PMID: 36109769
- PMCID: PMC9479353
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-022-02757-0
Genetic regulation of RNA splicing in human pancreatic islets
Abstract
Background: Non-coding genetic variants that influence gene transcription in pancreatic islets play a major role in the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes (T2D), and likely also contribute to type 1 diabetes (T1D) risk. For many loci, however, the mechanisms through which non-coding variants influence diabetes susceptibility are unknown.
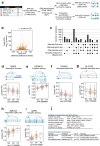
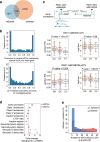
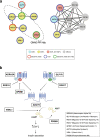
Results: We examine splicing QTLs (sQTLs) in pancreatic islets from 399 human donors and observe that common genetic variation has a widespread influence on the splicing of genes with established roles in islet biology and diabetes. In parallel, we profile expression QTLs (eQTLs) and use transcriptome-wide association as well as genetic co-localization studies to assign islet sQTLs or eQTLs to T2D and T1D susceptibility signals, many of which lack candidate effector genes. This analysis reveals biologically plausible mechanisms, including the association of T2D with an sQTL that creates a nonsense isoform in ERO1B, a regulator of ER-stress and proinsulin biosynthesis. The expanded list of T2D risk effector genes reveals overrepresented pathways, including regulators of G-protein-mediated cAMP production. The analysis of sQTLs also reveals candidate effector genes for T1D susceptibility such as DCLRE1B, a senescence regulator, and lncRNA MEG3.
Conclusions: These data expose widespread effects of common genetic variants on RNA splicing in pancreatic islets. The results support a role for splicing variation in diabetes susceptibility, and offer a new set of genetic targets with potential therapeutic benefit.
Keywords: Beta cells; CTRB2; Diabetes pathophysiology; G-protein signaling; Pancreatic beta-cells; Pancreatic islets; Quantitative trait loci; RNA splicing; Senescence; TWAS; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ALG’s spouse is an employee of Genentech and holds stock options in Roche. JAT is a member of the GSK Human Genetics Advisory Board.
Figures


References
-
- Mahajan A, Taliun D, Thurner M, Robertson NR, Torres JM, Rayner NW, Payne AJ, Steinthorsdottir V, Scott RA, Grarup N, et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat Genet. 2018;50:1505–1513. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0241-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vujkovic M, Keaton JM, Lynch JA, Miller DR, Zhou J, Tcheandjieu C, Huffman JE, Assimes TL, Lorenz K, Zhu X, et al. Discovery of 318 new risk loci for type 2 diabetes and related vascular outcomes among 1.4 million participants in a multi-ancestry meta-analysis. Nat Genet. 2020;52:680–691. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0637-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robertson CC, Inshaw JRJ, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Chen WM, Santa Cruz DF, Yang H, Cutler AJ, Crouch DJM, Farber E, Bridges SL, et al. Fine-mapping, trans-ancestral and genomic analyses identify causal variants, cells, genes and drug targets for type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2021;53:962–971. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00880-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

