Recent advances of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 36110206
- PMCID: PMC9468880
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.970699
Recent advances of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
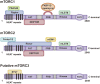
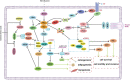
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine/threonine kinase involved in a variety of cellular functions, such as cell proliferation, metabolism, autophagy, survival and cytoskeletal organization. Furthermore, mTOR is made up of three multisubunit complexes, mTOR complex 1, mTOR complex 2, and putative mTOR complex 3. In recent years, increasing evidence has suggested that mTOR plays important roles in the differentiation and immune responses of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In addition, mTOR is a vital regulator of pivotal cellular and physiological functions, such as cell metabolism, survival and ageing, where it has emerged as a novel therapeutic target for ageing-related diseases. Therefore, the mTOR signaling may develop a large impact on the treatment of ageing-related diseases with MSCs. In this review, we discuss prospects for future research in this field.
Keywords: ageing-related diseases; differentiation; immune response; mTOR; mesenchymal stem cells; therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2022 Cai, Wang, Tang, Ke and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) as a potential therapeutic target in various diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2017 Jun;25(3):293-312. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0336-1. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Inflammopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28417246 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived IL-6 activates AMPK/mTOR signaling to inhibit the proliferation of reactive astrocytes induced by hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Exp Neurol. 2019 Jan;311:15-32. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30213506
-
mTOR signaling in stem and progenitor cells.Development. 2018 Jan 8;145(1):dev152595. doi: 10.1242/dev.152595. Development. 2018. PMID: 29311260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of autophagy and mTOR signaling in neural differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Biol Int. 2014 Nov;38(11):1337-43. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10320. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Cell Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 24890505
-
IFN-γ orchestrates mesenchymal stem cell plasticity through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and 3 and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 May;139(5):1667-1676. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27670240
Cited by
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells in intimal hyperplasia, an update.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1081881. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1081881. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

