Genetic Characteristics and Variation Spectrum of USH2A-Related Retinitis Pigmentosa and Usher Syndrome
- PMID: 36110214
- PMCID: PMC9468824
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.900548
Genetic Characteristics and Variation Spectrum of USH2A-Related Retinitis Pigmentosa and Usher Syndrome
Abstract
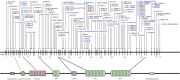
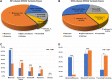
Purposes: We aimed to characterize the USH2A genotypic spectrum in a Chinese cohort and provide a detailed genetic profile for Chinese patients with USH2A-IRD. Methods: We designed a retrospective study wherein a total of 1,334 patients diagnosed with IRD were included as a study cohort, namely 1,278 RP and 56 USH patients, as well as other types of IEDs patients and healthy family members as a control cohort. The genotype-phenotype correlation of all participants with USH2A variant was evaluated. Results: Etiological mutations in USH2A, the most common cause of RP and USH, were found in 16.34% (n = 218) genetically solved IRD patients, with prevalences of 14.87% (190/1,278) and 50% (28/56). After bioinformatics and QC processing, 768 distinct USH2A variants were detected in all participants, including 136 disease-causing mutations present in 665 alleles, distributed in 5.81% of all participants. Of these 136 mutations, 43 were novel, nine were founder mutations, and two hot spot mutations with allele count ≥10. Furthermore, 38.5% (84/218) of genetically solved USH2A-IRD patients were caused by at least one of both c.2802T>G and c.8559-2 A>G mutations, and 36.9% and 69.6% of the alleles in the RP and USH groups were truncating, respectively. Conclusion: USH2A-related East Asian-specific founder and hot spot mutations were the major causes for Chinese RP and USH patients. Our study systematically delineated the genotype spectrum of USH2A-IRD, enabled accurate genetic diagnosis, and provided East Asian and other ethnicities with baseline data of a Chinese origin, which would better serve genetic counseling and therapeutic targets selection.
Keywords: USH; USH2A gene; founder mutations; genetic profile; rp.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Jiang, Han, Gao, Yang, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang, Gao, Wu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adato A., Lefèvre G., Delprat B., Michel V., Michalski N., Chardenoux S., et al. (2005). Usherin, the defective protein in Usher syndrome type IIA, is likely to be a component of interstereocilia ankle links in the inner ear sensory cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 3921–3932. 10.1093/hmg/ddi416 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

