Predicting prognosis and immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma based on N7-methylguanosine-related long noncoding RNAs
- PMID: 36110218
- PMCID: PMC9468367
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.930446
Predicting prognosis and immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma based on N7-methylguanosine-related long noncoding RNAs
Abstract
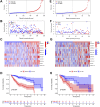
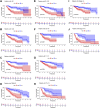
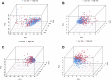
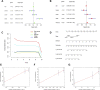
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which has high rates of recurrence and metastasis and is the main reason and the most common tumor for cancer mortality worldwide, has an unfavorable prognosis. N7-methylguanosine (m7G) modification can affect the formation and development of tumors by affecting gene expression and other biological processes. In addition, many previous studies have confirmed the unique function of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumor progression; however, studies exploring the functions of m7G-related lncRNAs in HCC patients has been limited. Methods: Relevant RNA expression information was acquired from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA, https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov), and m7G-related lncRNAs were identified via gene coexpression analysis. Afterward, univariate Cox regression, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, and multivariate regression analyses were implemented to construct an ideal risk model whose validity was verified using Kaplan-Meier survival, principal component, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and nomogram analyses. In addition, the potential functions of lncRNAs in the novel signature were explored through Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). At last, in both risk groups and subtypes classified based on the expression of the risk-related lncRNAs, we analyzed the immune characteristics and drug sensitivity of patients. Results: After rigorous screening processes, we built a model based on 11 m7G-related lncRNAs for predicting patient overall survival (OS). The results suggested that the survival status of patients with high-risk scores was lower than that of patients with low-risk scores, and a high-risk score was related to malignant clinical features. Cox regression analysis showed that the m7G risk score was an independent prognostic parameter. Moreover, immune cell infiltration and immunotherapy sensitivity differed between the risk groups. Conclusion: The m7G risk score model constructed based on 11 m7G-related lncRNAs can effectively assess the OS of HCC patients and may offer support for making individualized treatment and immunotherapy decisions for HCC patients.
Keywords: N7-methylguanosine; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune responses; lncRNA; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Gao, Chen, Liu, Zeng, Zhou and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of nine m7G-related lncRNAs as prognosis factors in tumor immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental validation.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 23;13:929035. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.929035. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36081998 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of prognostic signature of breast cancer based on N7-Methylguanosine-Related LncRNAs and prediction of immune response.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 24;13:991162. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.991162. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36353118 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic signature for mucinous colonic adenocarcinoma based on N7-methylguanosine-related long non-coding RNAs.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Feb 29;15(1):203-219. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-980. Epub 2024 Feb 28. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38482248 Free PMC article.
-
N7-methylguanosine modification in cancers: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Jan 29;18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01665-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39881381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M7G-related tumor immunity: novel insights of RNA modification and potential therapeutic targets.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 27;20(4):1238-1255. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.90382. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38385078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of N7-methylguanosine-related lncRNAs for the risk stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jun 30;14(3):1392-1411. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-227. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37435203 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

