Clinicopathological Implications of ASAP1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36110251
- PMCID: PMC9468229
- DOI: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610635
Clinicopathological Implications of ASAP1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
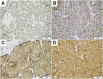
Background: The expression of ArfGAP with SH3 domain ankyrin repeat and PH domain 1 (ASAP1) is increased in various types of cancer, showing potential as a prognostic marker. The clinicopathological implications of ASAP1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. We thus investigated the clinicopathological significance and prognostic effect of ASAP1 expression in HCC patients. Materials and Methods: ASAP1 expression was assessed in 149 HCC tissue samples using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The associations between ASAP1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed. The prognostic effect of ASAP1 expression in patients with HCC was evaluated based on survival analyses and confirmed using a web-based tool. Results: ASAP1 expression was observed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. High ASAP1 expression was observed in 89 (59.7%) of 149 cases. High ASAP1 expression was significantly associated with male patients (p = 0.018), higher histological grade (p = 0.013), vessel invasion (p = 0.021), and higher stage (p = 0.020). High ASAP1 expression was associated with shorter overall survival (OS; p = 0.041) and recurrence-free survival (RFS; p = 0.008) based on Kaplan-Meier survival analyses. Web-based analysis using Kaplan-Meier (KM) plotter showed high mRNA ASAP1 expression to be associated with short OS (p = 0.001). Conclusion: High ASAP1 expression was associated with aggressive clinicopathological characteristics and poor clinical outcomes in patients with HCC. ASAP1 can be considered a prognostic biomarker in HCC patients.
Keywords: ASAP1; ArfGAP with SH3 domain ankyrin repeat and PH domain 1; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunohistochemistry; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Bang, Jee, Son, Cha, Sim, Kim, Park, Myung, Kim and Paik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

