Oral Self-Mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: A Case Report
- PMID: 36110449
- PMCID: PMC9463611
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.27874
Oral Self-Mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: A Case Report
Abstract
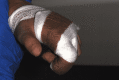
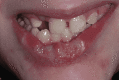
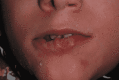
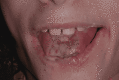
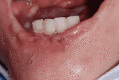
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is an inherited recessive X-related disorder caused by a deficiency of the purine salvage enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. It is characterized by dystonia and compulsive self-mutilation, in particular, biting behavior on the oral mucosa, tongue, lips, fingers, and shoulders, typically before one year of age. The majority of these patients require several procedures, including dental extractions, to prevent significant secondary lesions. This article aims to report a clinical case of a 12-year-old boy with an LNS diagnosis who was referred to the Paediatric Stomatology Department of Central Lisbon University Hospital. Since the age of eight, the patient had displayed self-harm behavior, with arm and oral injuries. On evaluation, he presented with deep ulcerated lesions on the lips and tongue, with substance loss associated with a significant decrease in food intake and consequent weight loss. The management included conservative therapy with gabapentin, lorazepam, and botulinum toxin injections. A successful reduction of self-mutilation with no signs of new lesions in the oral cavity and an improvement in nutritional status were reported. The therapeutic approach is essential to provide the best quality of life for patients and their caregivers. To delay radical treatments, multiple therapeutic options can be used. The oral pathology team considered that the most appropriate therapy was botulinum toxin A injections along with therapeutic adjustment, which was effective in wound healing and self-mutilation behavior ceasing at the two-month follow-up.
Keywords: dental care for children; lesch-nyhan syndrome; lip injuries; self-biting; self-mutilation.
Copyright © 2022, Ferrão et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome and Oral Self-injury: A Systematic Review of Case Reports.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Dec;17(12):1431-1438. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2990. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39867109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral self-mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome. Case Report.Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018 Feb;89(1):86-91. doi: 10.4067/S0370-41062018000100086. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29664508 English, Spanish.
-
Botulinum toxin as a novel treatment for self-mutilation in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005 Sep;47(9):636-9. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16138673
-
Botulinum toxin: treatment of self-mutilation in patients with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.Clin Neuropharmacol. 2008 May-Jun;31(3):180-3. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0b013e31814a62cc. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18520986
-
Normal uricemia in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome and the association with pulmonary embolism in a young child-a case report and literature review.Pediatr Neonatol. 2014 Aug;55(4):312-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2012.12.016. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Pediatr Neonatol. 2014. PMID: 23597535 Review.
Cited by
-
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome and Oral Self-injury: A Systematic Review of Case Reports.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Dec;17(12):1431-1438. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2990. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39867109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-mutilation: a systematic review.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025 Mar;21(1):430-442. doi: 10.1007/s12024-024-00809-4. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2025. PMID: 38613622
References
-
- A familial disorder of uric acid metabolism and central nervous system function. Lesch M, Nyhan WL. Am J Med. 1964;36:561–570. - PubMed
-
- Prevention of self-mutilation in patients with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: review of literature. Cusumano FJ, Penna KJ, Panossian G. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11693008/ ASDC J Dent Child. 2001;68:175–178. - PubMed
-
- The spectrum of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) deficiency. Clinical experience based on 22 patients from 18 Spanish families. Puig JG, Torres RJ, Mateos FA, Ramos TH, Arcas JM, Buño AS, O'Neill P. Medicine (Baltimore) 2001;80:102–112. - PubMed
-
- Antero-ventral internal pallidum stimulation improves behavioral disorders in Lesch-Nyhan disease. Cif L, Biolsi B, Gavarini S, et al. Mov Disord. 2007;22:2126–2129. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
