Renal Function in Hypertensive Patients Receiving Cilnidipine and L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled and Retrospective Studies
- PMID: 36110460
- PMCID: PMC9461693
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.27847
Renal Function in Hypertensive Patients Receiving Cilnidipine and L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled and Retrospective Studies
Abstract
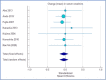
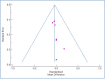
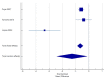
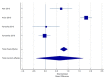
Nearly 65%-95% of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients have hypertension. Calcium-channel blockers are the first-line drugs for the treatment of hypertension, including hypertension with diabetes. This study aims to estimate the effect of an L-type calcium channel blocker (CCB), cilnidipine, on the renal function of hypertensive patients. Randomized control trials were selected from PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Science Direct, Elton B. Stephens Company (EBSCO), Springer, Ovid, Cochrane Library, Medline, VIP, and Wanfang databases (from the date of databases' establishment till January 2022). Data were independently evaluated following the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. The changes in serum creatinine (SCr), urinary protein excretion (UPE), urinary protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) before and after treatment, in percentages, were extracted for the meta-analysis. The mean difference (MD) and a CI of 95% were determined using RevMan 5.3 software. A total of 11 studies were analyzed. The standardized mean difference (SMD) between cilnidipine and L-type CCBs was -0.022, suggesting a reduced SCr with cilnidipine. For UPCR, the SMD value is 1.28. Although cilnidipine reduced UPCR in all four studies, the L-type CCBs reported a slight increase in UPCR. For eGFR, the SMD value was found to be 0.693. Cilnidipine had a more favorable effect on eGFR when compared to the L-type CCBs. While cilnidipine had similar effects on SCr to that of L-type CCBs, cilnidipine showed greater improvement in UPCR, UPE, and eGFR values.
Keywords: cilnidipine; hypertensive; l-type ccbs; meta-analysis; renal function.
Copyright © 2022, Srivathsan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cilnidipine: An L- and N-Type Blocker of Calcium Channels Ameliorating Renal Damage in Experimental Hypertensive Rats.Cureus. 2025 Mar 29;17(3):e81404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81404. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40296922 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure Reducing Potential and Renoprotective Action of Cilnidipine Among Hypertensive Patients Suffering From Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2023 Apr 18;15(4):e37774. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37774. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37213948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Cilnidipine (L/N-type Calcium Channel Blocker) in Treatment of Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2021 Nov 22;13(11):e19822. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19822. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34963839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switching to an L/N-type calcium channel blocker shows renoprotective effects in patients with chronic kidney disease: the Kyoto Cilnidipine Study.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(4):1417-28. doi: 10.1177/147323001204000420. J Int Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22971493 Clinical Trial.
-
L/N-type calcium channel blocker cilnidipine added to renin-angiotensin inhibition improves ambulatory blood pressure profile and suppresses cardiac hypertrophy in hypertension with chronic kidney disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 16;14(8):16866-81. doi: 10.3390/ijms140816866. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23959116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Cilnidipine: An L- and N-Type Blocker of Calcium Channels Ameliorating Renal Damage in Experimental Hypertensive Rats.Cureus. 2025 Mar 29;17(3):e81404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81404. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40296922 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure Reducing Potential and Renoprotective Action of Cilnidipine Among Hypertensive Patients Suffering From Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2023 Apr 18;15(4):e37774. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37774. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37213948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Drug Prescription in Newly Diagnosed Hypertension Patients in India.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025 Jan;27(1):e14963. doi: 10.1111/jch.14963. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025. PMID: 39822165 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive effect of sinapine extracted from rapeseed meal in 2K1C hypertensive rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 3;15(1):4133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88926-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39900955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sympathetic nerve activity in end-stage renal disease. Hausberg M, Kosch M, Harmelink P, et al. Circulation. 2002;106:1974–1979. - PubMed
-
- Long-term blockade of L/N-type Ca(2+) channels by cilnidipine ameliorates repolarization abnormality of the canine hypertrophied heart. Takahara A, Nakamura Y, Wagatsuma H, et al. http://2009. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;158:1366–1374. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Comparison between cilnidipine and amlodipine besilate with respect to proteinuria in hypertensive patients with renal diseases. Kojima S, Shida M, Yokoyama H. Hypertens Res. 2004;27:379–385. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
