Exploring potential mechanism of ciwujia tablets for insomnia by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS, network pharmacology, and experimental validation
- PMID: 36110515
- PMCID: PMC9468710
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.990996
Exploring potential mechanism of ciwujia tablets for insomnia by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS, network pharmacology, and experimental validation
Abstract
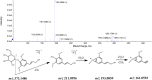
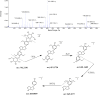
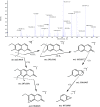
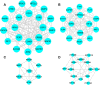
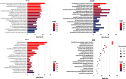
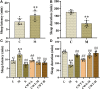
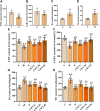
Insomnia, whether chronic or intermittent, is a common central nervous system disease. Ciwujia Tablet (CWT) is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) made from the extract of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim. This medication is commonly used for treating insomnia in China, but the lack of in-depth research focused on the chemical ingredients of CWT creates a gap in knowledge regarding its effective constituents against insomnia. Considering that the therapeutic material basis, targets, and pathways related to this drug have not been fully investigated by scholars in the field, the focus of this study is on identifying the chemical ingredients or structural characteristics of CWT by the UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS technique. Besides, concepts of network pharmacology were also used to investigate the targets and pathways of CWT. An insomnia rat model was established by intraperitoneal injection of p-chlorophenylalanine, and the results were verified through various experiments. A total of 46 ingredients were identified in CWT, such as eleutheroside B, eleutheroside E, isofraxidin, and chlorogenic acid. Among them, 17 ingredients with good solubility, favorable gastrointestinal absorption, and high bioavailability were selected for network pharmacological analysis. It was concluded that CWT participated in the regulation of neurotransmitter levels, modulation of ion transport, neurotransmitter receptor activity, synaptic transmission, dopaminergic transmission and other essential processes. Results from the animal experiments showed that CWT can increase the content of inhibitory neurotransmitters 5-HT and GABA in the brain, reduce the synthesis of excitatory escalating transmitters DA and NE, shorten the sleep latency and prolong the sleep duration of insomnia rats. Furthermore, CWT could significantly alleviate the symptoms of insomnia in model rats. Identifying the chemical ingredients of CWT in this experiment is of great significance for exploring its potential curative effects, which provides a solid basis for further understanding the therapeutic value of this medication.
Keywords: UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS; ciwujia tablet; insomnia; nervous system disease; neurotransmitter.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Yang, Wan, Li, Yan, Han, Sun and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the pharmacological effects and exploration of the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine preparation Ciwujia tablets in treating insomnia based on ethology, energy metabolism, and urine metabolomic approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1009668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1009668. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36545309 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of five neurotransmitters in the rat brain for the study of the hypnotic effects of Ziziphi Spinosae Semen aqueous extract on insomnia rat model by UPLC-MS/MS.Chin J Nat Med. 2019 Jul;17(7):551-560. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30077-9. Chin J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 31514987
-
Mass spectrometry-based urinary metabolomics for the investigation on the mechanism of action of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim. leaves against ischemic stroke in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;241:111969. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111969. Epub 2019 May 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31125596
-
A review on the immunomodulatory activity of Acanthopanax senticosus and its active components.Chin Med. 2019 Jul 31;14:25. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0250-0. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31388349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panax Notoginseng Saponins: A Review of Its Mechanisms of Antidepressant or Anxiolytic Effects and Network Analysis on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Molecules. 2018 Apr 17;23(4):940. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040940. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29673237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the pharmacological effects and exploration of the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine preparation Ciwujia tablets in treating insomnia based on ethology, energy metabolism, and urine metabolomic approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1009668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1009668. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36545309 Free PMC article.
-
Potential mechanism of Luoshi Neiyi prescription in endometriosis based on serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1395160. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1395160. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39135784 Free PMC article.
-
A dicoumarol-graphene oxide quantum dot polymer inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus through the JAK-STAT signaling pathway.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1417404. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1417404. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38962129 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Chemical Components Analysis of Periplocae Cortex, Lycii Cortex, and Acanthopanacis Cortex Based on Mass Spectrometry Data and Chemometrics.Molecules. 2024 Aug 11;29(16):3807. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163807. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202886 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Effects of Grafting on Special Metabolites of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves.Molecules. 2023 Jun 20;28(12):4877. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124877. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375432 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

