Akebia saponin D protects hippocampal neurogenesis from microglia-mediated inflammation and ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway
- PMID: 36110522
- PMCID: PMC9468712
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.927419
Akebia saponin D protects hippocampal neurogenesis from microglia-mediated inflammation and ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway
Abstract
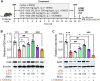
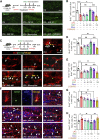
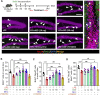
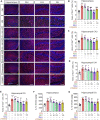
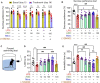
Given the ability of akebia saponin D (ASD) to protect various types of stem cells, in the present study, we hypothesized that ASD could promote the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of neural stem/precursor cells (NSPCs), even in a microglia-mediated inflammatory environment, thereby mitigating inflammation-related neuropsychopathology. We established a mouse model of chronic neuroinflammation by exposing animals to low-dose lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 0.25 mg/kg/d) for 14 days. The results showed that chronic exposure to LPS strikingly reduced hippocampal levels of PI3K and pAkt and neurogenesis in mice. In the presen of a microglia-mediated inflammatory niche, the PI3K-Akt signaling in cultured NSPCs was inhibited, promoting their apoptosis and differentiation into astrocytes, while decreasing neurogenesis. Conversely, ASD strongly increased the levels of PI3K and pAkt and stimulated NSPC proliferation, survival and neuronal differentiation in the microglia-mediated inflammatory niche in vitro and in vivo. ASD also restored the synaptic function of hippocampal neurons and ameliorated depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in mice chronically exposed to LPS. The results from network pharmacology analysis showed that the PI3K-AKT pathway is one of the targets of ASD to against major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety and Alzheimer's disease (AD). And the results from molecular docking based on computer modeling showed that ASD is bound to the interaction interface of the PI3K and AKT. The PI3K-Akt inhibitor LY294002 blocked the therapeutic effects of ASD in vitro and in vivo. These results suggested that ASD protects NSPCs from the microglia-mediated inflammatory niche, promoting their proliferation, survival and neuronal differentiation, as well as ameliorating depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors and cognitive impairment by activating the PI3K-AKT pathway. Our work suggests the potential of ASD for treating Alzheimer's disease, depression and other cognitive disorders involving impaired neurogenesis by microglia-mediated inflammation.
Keywords: PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; akebia saponin D; cognitive impairment; depression; microglia; neural stem/precursor cell; neurogenesis; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhang, Xiao, Su, Li, Yang, Zhao, Jiang, You and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Alavi S., Darharaj M., Bilehsavar S. H., Amini M., Zafarghandi M. B. S., Berenji V., et al. (2021). Successful use of minocycline for the treatment of methamphetamine-induced psychosis and cognitive impairments: An open-label case series. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 44, 126–131. 10.1097/WNF.0000000000000460 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bassani T. B., Bonato J. M., Machado M. M. F., Cóppola-Segovia V., Moura E. L. R., Zanata S. M., et al. (2018). Decrease in adult neurogenesis and neuroinflammation are involved in spatial memory impairment in the streptozotocin-induced model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 4280–4296. 10.1007/s12035-017-0645-9 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

