Linezolid resistance in multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36110536
- PMCID: PMC9468755
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.955050
Linezolid resistance in multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
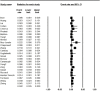
Introduction: Linezolid (LNZ) is an effective antibiotic to treat patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) treatment failure. M. tuberculosis strains resistant to isoniazid and rifampin are defined as MDR-TB. In recent years, resistance to LNZ among MDR-TB cases has been reported in several different countries. In this study, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the prevalence of LNZ resistance among MDR-TB isolates. Methods: The databases of Embase, PubMed/Medline, and Web of Science were searched systematically from January 2000 to April 2021. Statistical analyses were performed by using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software. Heterogeneity was reported by using the t-squared statistic and Q-statistic. Begg's rank correlation in combination with the funnel plot were used to evaluate any possible publication bias. Results: In total, 25 studies were selected for meta-analysis from 14 different countries; the majority was from China (n = 5) and Turkey (n = 4). Moreover, 7,366 patients were infected with MDR M. tuberculosis. Among the study population, 98 patients were co-infected with HIV, and 18 patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV). Furthermore, 28 cases had diabetes, and139 cases were alcohol abuser. Overall, 4,956 MDR M. tuberculosis strains were isolated from TB patients. The pooled frequency of LNZ resistance among the clinical isolates of MDR M. tuberculosis was 4.2% (95%). Begg's (p = 0.72) test showed no evidence of publication bias. Conclusion: LNZ resistance among MDR M. tuberculosis isolates is increasing. On the other hand, long-term treatment of MDR-TB cases with LNZ alone is associated with several adverse effects. Thus, it is recommended that newer anti-TB drugs, including bedaquiline and delamanid, in combination with linezolid could increase its effectiveness and decrease toxicities. However, more studies should be done in this field.
Keywords: MDR-TB; TB; linezolid; meta-analysis; resistance; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2022 Azimi, Khoshnood, Asadi, Heidary, Mahmoudi, Kaviar, Hallajzadeh and Nasiri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beijing genotype of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is significantly associated with linezolid resistance in multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in China.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014 Mar;43(3):231-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.12.007. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014. PMID: 24439458
-
Linezolid resistance among multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates in Iran.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2021 Jun 24. doi: 10.1556/030.2021.01490. Online ahead of print. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2021. PMID: 34174037
-
Prevalence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant to bedaquiline and delamanid in China.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Sep;26:241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.06.007. Epub 2021 Jun 30. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021. PMID: 34214699
-
Association between diabetes mellitus and multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 15;7(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0828-0. Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30322409 Free PMC article.
-
An updated systematic review and meta-analysis on Mycobacterium tuberculosis antibiotic resistance in Iran (2013-2020).Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Apr;24(4):428-436. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.48628.11161. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34094023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Linezolid in Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients: Clinical Factors and Hematological Toxicities.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 20;17:2531-2540. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S464429. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38933777 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid resistance in patients with drug-resistant TB.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2023 Jul 1;27(7):567-569. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.22.0632. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2023. PMID: 37353865 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mechanisms of Linezolid Resistance in Mycobacteria.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 24;16(6):784. doi: 10.3390/ph16060784. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relapse after treatment with standardized all-oral short regimens for rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis (RR-TB): A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024 Mar 3;35:100426. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2024.100426. eCollection 2024 May. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024. PMID: 38468818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF SILVER NANOCOMPOSITES ON RIFAMPICIN-RESISTANT M. TUBERCULOSIS STRAINS.Georgian Med News. 2024 Jun;(351):102-108. Georgian Med News. 2024. PMID: 39230231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed I., Jabeen K., Inayat R., Hasan R. (2013). Susceptibility testing of extensively drug-resistant and pre-extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis against levofloxacin, linezolid, and amoxicillin-clavulanate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57 (6), 2522–2525. 10.1128/AAC.02020-12 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alcalá L., Ruiz-Serrano M. J., Turégano C. P-F., De Viedma D. G., Díaz-Infantes M., Marin-Arriaza M., et al. (2003). In vitro activities of linezolid against clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that are susceptible or resistant to first-line antituberculous drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47 (1), 416–417. 10.1128/aac.47.1.416-417.2003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azimi T., Shariati A., Fallah F., Imani Fooladi A. A., Hashemi A., Goudarzi H., et al. (2017). Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotyping using MIRU-VNTR typing. J. Mazandaran Univ. Med. Sci. 27 (149), 40–48.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

