Pivotal role of vitamin D in mitochondrial health, cardiac function, and human reproduction
- PMID: 36110560
- PMCID: PMC9441677
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2022-4935
Pivotal role of vitamin D in mitochondrial health, cardiac function, and human reproduction
Abstract
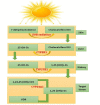
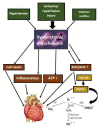
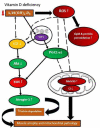
Vitamin D, a secosteroid hormone, appears to have significant beneficial effects on various physiological systems, including the musculoskeletal system. Vitamin D assists in the regulation of numerous critical biological functions and physiological processes in humans, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial respiration, and is also linked to cardiac diseases. It is also reported that vitamin D plays a central role in molecular and cellular mechanisms, which reduce oxidative stress, and tissue damage and regulate cellular health. On the other side, hypovitaminosis D reduces mitochondrial activity and increases oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Hypervitaminosis D increases the prevalence and severity of cellular damage. It has also been reported that vitamin D is involved in many functions of the reproductive system in human and critically play an important role in the reproductive tissues of women and men. Its role is very well defined, starting from female menarche to menopause, pregnancy, and lactation, and finally in male fertility. Hence, the appropriate amount of vitamin D is necessary to maintain the normal function of cell organelles. Based on recent studies, it is understood that vitamin D is involved in the biological activities of mitochondria in cells, especially in cardiomyocytes. In this review, we emphasized the role of vitamin D in mitochondrial respiration, which could significantly influence heart health and human reproduction.
Keywords: Vitamin D; cardiac diseases; cell damage; inflammation; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2022 Matta Reddy et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vitamin D Deficiency: Effects on Oxidative Stress, Epigenetics, Gene Regulation, and Aging.Biology (Basel). 2019 May 11;8(2):30. doi: 10.3390/biology8020030. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31083546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D: a Review of its Effects on Epigenetics and Gene Regulation.Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2020 Dec 31;62(4):662-667. doi: 10.3897/folmed.62.e50204.. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2020. PMID: 33415918 Review.
-
Vitamin D: the secosteroid hormone and human reproduction.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2007 Jan;23(1):13-24. doi: 10.1080/09513590601045629. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17484507 Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Role of oxidative stress in female reproduction.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005 Jul 14;3:28. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-28. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16018814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tremendous Fidelity of Vitamin D3 in Age-related Neurological Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):7211-7238. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03989-w. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38372958 Review.
-
Vitamin D Determinants, Status, and Antioxidant/Anti-inflammatory-Related Effects in Cardiovascular Risk and Disease: Not the Last Word in the Controversy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;12(4):948. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040948. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose tissue as target of environmental toxicants: focus on mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative inflammation in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 May;480(5):2863-2879. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05165-z. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39704874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five Years of Long COVID Syndrome: An Updated Review on Cardiometabolic and Psychiatric Aspects.Cardiol Res. 2025 Apr;16(2):81-85. doi: 10.14740/cr2014. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Cardiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40051665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Prognostic Value of 10 Biochemical Indices at Admission for Prediction Postoperative Myocardial Injury and Hospital Mortality in Patients with Osteoporotic Hip Fracture.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 16;11(22):6784. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226784. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas MA. Physiological functions of Vitamin D in adipose tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;165:369–381. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Hynson JE, Hecht TJ, Light RP, Sinha AD. Short-term vitamin D receptor activation increases serum creatinine due to increased production with no effect on the glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int. 2011;80:1073–1079. - PubMed
-
- Allsworth JE, Peipert JF. Prevalence of bacterial vaginosis: 2001–2004 national health and nutrition examination survey data. Obstetr Gynecol. 2007;109:114–120. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
