Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 - A Surge of CoronaVirus Disease-2019: An Epidemiological Study in Coimbatore District
- PMID: 36110629
- PMCID: PMC9469229
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_124_22
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 - A Surge of CoronaVirus Disease-2019: An Epidemiological Study in Coimbatore District
Abstract
Context: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) is an ongoing pneumonia-like cluster syndrome which originated in Wuhan city of China and is still now on escalation, causing severe outbreaks all over the world. Being a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus which has the low proofreading RNA-dependent RNA polymerase leads to many mutations and that serves as the major cause for the progress of the disease. As per the recent research works done, 99% of COVID-19 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) are due to pangolin-associated coronavirus which causes the super spreading events of coronavirus. SARS-CoV-2 was identified in the nasopharyngeal swabs received in the viral transport medium at optimum temperature.
Materials and methods: The tests were conducted for a time period of 1 year from July 2020 to June 2021. A total of 77,824 samples were tested in the laboratory as per ICMR guidelines using approved RNA extraction kits and polymerase chain reaction kits.
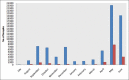
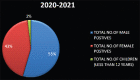
Results: In the total of 77,824 samples tested in our laboratory, 14174 positives were identified. In that, about seven positive cases (0.004%) were identified in the month of July 2020 which increased to the maximum in September 2020 to about 865 positive cases (6%) which is the peak of first wave COVID-19 in Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu. Out of 77,824 samples tested, the actual cumulative laboratory-confirmed positive cases of about 14174 were identified. In that, 7731 (55%) male positive cases were identified, 6171 (43%) female positive cases were identified, and 270 (2%) children who were below 12 years of age also were tested positive.
Conclusions: The findings of the study indicated a high predominance of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the male gender population when compared to females and children below 12 years of age in Coimbatore district as of June 2021. The surge of cases was high in September 2020 as well as in May 2021, indicating the first and second wave of COVID-19.
Keywords: Mutation; nasopharyngeal swab; ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; viral transport medium.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection and analysis of nucleic acid in various biological samples of COVID-19 patients.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Sep-Oct;37:101673. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101673. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32311437 Free PMC article.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19 Cases and their Correlation with S.LDH Levels- An Observational Study from Southeast Rajasthan.J Assoc Physicians India. 2021 Sep;69(9):11-12. J Assoc Physicians India. 2021. PMID: 34585882
-
The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):833-840. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25825. Epub 2020 Apr 25. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32243607
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2) infection during late pregnancy: a report of 18 patients from Wuhan, China.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 Jul 8;20(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-03026-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32641013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus Update (Live): 316,662 Cases and 13,599 Deaths from COVID-19 Virus Outbreak. [Last accessed on 2020 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Reports. [Last accessed on 2020 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous