Duplex Hemodynamic Parameters of Both Superior and Inferior Thyroid Arteries in Evaluation of Thyroid Hyperfunction Disorders
- PMID: 36110917
- PMCID: PMC9470082
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S375016
Duplex Hemodynamic Parameters of Both Superior and Inferior Thyroid Arteries in Evaluation of Thyroid Hyperfunction Disorders
Abstract
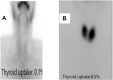
Background: Thyrotoxicosis may be caused by Graves' disease or destructive thyroiditis. Differentiation between causes of thyrotoxicosis is crucial as management will differ. 99mTechnetium (Tc)-pertechnetate thyroid scintigraphy is currently the gold standard for this purpose, however, is expensive and uses ionizing radiation.
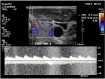
Objective: To evaluate the role of color flow Doppler Ultrasound (CDU) of the superior thyroid (STA) and inferior thyroid arteries (ITA) as an inexpensive, non-invasive tool that can aid in differentiating between Graves' disease and thyroiditis and compare it with thyroid scintigraphy.
Methods: Sixty-nine patients with newly-diagnosed thyrotoxicosis and 30 controls were enrolled. Thyroid functions, thyroid scintigraphy, and CDU of STA and ITA with measurements of peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV), were performed. According to thyroid scintigraphy results, patients were divided into two groups: 42 patients with Graves' disease and 27 patients with thyroiditis.
Results: PSV and EDV of both STA and ITA were significantly higher in patients with Graves' disease than thyroiditis (p-values <0.001). The STA-PSV had an equal sensitivity and specificity of 66.7%; cut-off value 76.57 cm/s, while those of STA-EDV were 73.8%, and 77.8% respectively; cut-off value 28.22 cm/s. ITA-PSV had a sensitivity and specificity of 76.2% and 77.8%, respectively; cut-off value 62.12 cm/s), while those of ITA-EDV were 78.6% and 77.8%, respectively; cut-off value 5.22 cm/s.
Conclusion: CDU parameters of the STA and ITA could be used as an alternative to thyroid scintigraphy for discriminating between Graves' disease and thyroiditis.
Keywords: Color Doppler Flow Ultrasound; Graves’ disease; end-diastolic velocity; peak systolic velocity; thyroiditis.
© 2022 Assem Hussein et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A meta-analysis: elucidating diagnostic thresholds of peak systolic flow velocities in thyroid arteries for the discrimination of Graves' disease and destructive thyrotoxicosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 7;15:1393126. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1393126. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38911037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Utility of Mean Peak Systolic Velocity of Superior Thyroid Artery in Differentiating Graves' Disease from Thyroiditis.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2021 Apr;31(2):311-317. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1734360. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34556913 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between peak systolic velocity of the inferior thyroid artery and technetium-99m pertechnetate thyroid uptake in differentiating Graves' disease from thyroiditis.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 2;63(5):495-500. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000165. eCollection 2019. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31482952 Free PMC article.
-
Mean peak systolic velocity of the superior thyroid artery is correlated with radioactive iodine uptake in untreated thyrotoxicosis.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(2):640-7. doi: 10.1177/147323001204000226. J Int Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22613425
-
Development of Graves' Disease After SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 23;9:778964. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.778964. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34888290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A meta-analysis: elucidating diagnostic thresholds of peak systolic flow velocities in thyroid arteries for the discrimination of Graves' disease and destructive thyrotoxicosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 7;15:1393126. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1393126. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38911037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-infrared diffuse optical characterization of human thyroid using ultrasound-guided hybrid time-domain and diffuse correlation spectroscopies.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Nov 26;15(12):7035-7055. doi: 10.1364/BOE.538141. eCollection 2024 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 39679411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee JC. Thyroid scans. Aust Fam Physician. 2012;41(8):1–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

