XGBoost algorithm and logistic regression to predict the postoperative 5-year outcome in patients with glioma
- PMID: 36110992
- PMCID: PMC9469144
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-3384
XGBoost algorithm and logistic regression to predict the postoperative 5-year outcome in patients with glioma
Abstract
Background: Glioma is the most common primary intracranial tumor with poor prognosis. The prediction of glioma prognosis has not been well investigated. XGBoost algorithm has been widely used in and data analysis. The predictive value of XGBoost algorithm in glioma remains unclear. This current study used the XGBoost algorithm to construct a predictive model for postoperative outcomes of glioma patients.
Methods: Patients with glioma who underwent surgery from January 2006 to April 2017 were retrospectively included in this study. Clinical and follow-up data were collected. The XGBoost model and multivariate logistic regression analysis model were used to screen the factors related to postoperative outcomes, and the results of the two models were compared. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and Youden index were calculated to evaluate the predictive value of the XGBoost model.
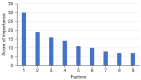
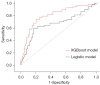
Results: A total of 638 patients were included. In total, 336 (52.7%) cases died within 5 years after the operation. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age, gender, World Health Organization (WHO) grade, extent of tumor resection, Karnofsy performance score (KPS), tumor diameter, and whether postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy were administered, were the most important risk factors for death within 5 years after surgery in glioma patients. The XGBoost model showed that the top 5 factors related to death of glioma patients within 5 years after surgery were WHO grade (30 points), extent of tumor resection (19 points), postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy (16 points), KPS (14 points), and age (11 points). The AUC of the XGBoost model for predicting the death of glioma patients within 5 years after surgery was 0.803 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.718-0.832], and the sensitivity and specificity were 0.894 and 0.581, respectively. The Youden index was 0.475. The AUC of the multivariate logistic regression model was 0.738 (95% CI: 0.704-0.781), the sensitivity and specificity were 0.785 and 0.632, respectively, and the Youden index was 0.417.
Conclusions: Compared with multivariate logistic regression model, XGBoost model has better performance in predicting the risk of death within 5 years after surgery in patients with glioma.
Keywords: Glioma; XGBoost model; death; multivariate logistic analysis; risk factors.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-3384/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
