Estimation of the minimum effective volume of 0.5% bupivacaine for ultrasound-guided popliteal sciatic nerve block in diabetic patients with neuropathy
- PMID: 36111092
- PMCID: PMC9469006
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_405_22
Estimation of the minimum effective volume of 0.5% bupivacaine for ultrasound-guided popliteal sciatic nerve block in diabetic patients with neuropathy
Abstract
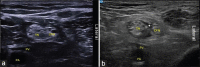
Background and aims: The safety of conventional regional nerve block techniques in patients with established neuropathies, such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), is still unclear. We designed this prospective dose finding study to identify the minimum effective local anaesthetic volume of 0.5% bupivacaine for ultrasound-guided subparaneural popliteal sciatic nerve block in 90% of DPN patients undergoing below-knee surgery (MELAV90).
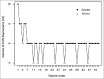
Methods: Fifty-three patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and scheduled for below knee surgical procedure received popliteal sciatic nerve block under ultrasound guidance. The initial local anaesthetic volume used was 10 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine. The subsequent local anaesthetic volume allocation was based on biased-coin-design. Accordingly, the local anaesthetic volume given to each subject was based on the block outcome of the previous patient. The study included patients prospectively until 45 successful blocks were obtained. The primary measurement was the minimum effective local anaesthetic volume resulting in a successful subparaneural popliteal sciatic nerve block in 90% of DPN patients. The MELAV90 was calculated using isotonic regression and a 95% confidence interval bootstrapping method.
Results: The study included 53 patients to obtain 45 successful blocks. The MELAV90 of 0.5% bupivacaine was obtained at 5.85 ml (95% confidence interval, 5.72 to 6.22 ml). Eight patients needed supplemental anaesthesia to complete the surgery. No other complications were noted.
Conclusion: For patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy undergoing below-knee surgery, the MELAV90 of 0.5% bupivacaine for subparaneural popliteal sciatic nerve to achieve surgical anaesthesia was 5.85 ml.
Keywords: Bupivacaine; diabetic neuropathy; minimum effective anaesthetic volume; nerve block; popliteal-sciatic nerve; ultrasound.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Boulton AJM. Diabetic neuropathy and foot complications. Zochodne DW, Malik RA, editors. Diabetes and the Nervous System. Elsevier. 2014:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Baeriswyl M, Taffé P, Kirkham KR, Bathory I, Rancati V, Crevoisier X, et al. Comparison of peripheral nerve blockade characteristics between non-diabetic patients and patients suffering from diabetic neuropathy:A prospective cohort study. Anaesthesia. 2018;73:1110–7. - PubMed
-
- Lirk P, Verhamme C, Boeckh R, Stevens MF, ten Hoope W, Gerner P, et al. Effects of early and late diabetic neuropathy on sciatic nerve block duration and neurotoxicity in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114:319–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
