Detection of Viral Infection and Bacterial Coinfection and Superinfection in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department Using the 29-mRNA Host Response Classifier IMX-BVN-3: A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 36111173
- PMCID: PMC9452140
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofac437
Detection of Viral Infection and Bacterial Coinfection and Superinfection in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department Using the 29-mRNA Host Response Classifier IMX-BVN-3: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: Identification of bacterial coinfection in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) facilitates appropriate initiation or withholding of antibiotics. The Inflammatix Bacterial Viral Noninfected (IMX-BVN) classifier determines the likelihood of bacterial and viral infections. In a multicenter study, we investigated whether IMX-BVN version 3 (IMX-BVN-3) identifies patients with COVID-19 and bacterial coinfections or superinfections.
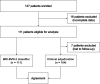
Methods: Patients with polymerase chain reaction-confirmed COVID-19 were enrolled in Berlin, Germany; Basel, Switzerland; and Cleveland, Ohio upon emergency department or hospital admission. PAXgene Blood RNA was extracted and 29 host mRNAs were quantified. IMX-BVN-3 categorized patients into very unlikely, unlikely, possible, and very likely bacterial and viral interpretation bands. IMX-BVN-3 results were compared with clinically adjudicated infection status.
Results: IMX-BVN-3 categorized 102 of 111 (91.9%) COVID-19 patients into very likely or possible, 7 (6.3%) into unlikely, and 2 (1.8%) into very unlikely viral bands. Approximately 94% of patients had IMX-BVN-3 unlikely or very unlikely bacterial results. Among 7 (6.3%) patients with possible (n = 4) or very likely (n = 3) bacterial results, 6 (85.7%) had clinically adjudicated bacterial coinfection or superinfection. Overall, 19 of 111 subjects for whom adjudication was performed had a bacterial infection; 7 of these showed a very likely or likely bacterial result in IMX-BVN-3.
Conclusions: IMX-BVN-3 identified COVID-19 patients as virally infected and identified bacterial coinfections and superinfections. Future studies will determine whether a point-of-care version of the classifier may improve the management of COVID-19 patients, including appropriate antibiotic use.
Keywords: COVID-19; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; bacterial infection; coinfection; superinfection; viral infection.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Wu CP, Adhi F, Highland K. Recognition and management of respiratory co-infection and secondary bacterial pneumonia in patients with COVID-19. Cleve Clin J Med 2020; 87:659–63. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Loeches I, Sanchez-Corral A, Diaz E, et al. Community-acquired respiratory coinfection in critically ill patients with pandemic 2009 influenza A(H1N1) virus. Chest 2011; 139:555–62. - PubMed