Extent of fibrosis and lung function decline in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease: data from the SENSCIS trial
- PMID: 36111858
- PMCID: PMC10152288
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac535
Extent of fibrosis and lung function decline in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease: data from the SENSCIS trial
Abstract
Objective: To assess associations between the extent of fibrotic interstitial lung disease (ILD) and forced vital capacity (FVC) at baseline and change in FVC over 52 weeks in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD) in the SENSCIS trial.
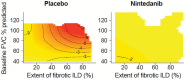
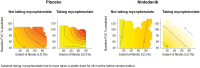
Material and methods: We used generalized additive models, which involve few assumptions and allow for interaction between non-linear effects, to assess associations between the extent of fibrotic ILD on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), and the interplay of extent of fibrotic ILD on HRCT and FVC % predicted, at baseline and FVC decline over 52 weeks.
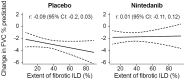
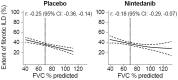
Results: In the placebo group (n = 288), there was weak evidence of a modest association between a greater extent of fibrotic ILD at baseline and a greater decline in FVC % predicted at week 52 [r: -0.09 (95% CI -0.2, 0.03)]. Higher values of both the extent of fibrotic ILD and FVC % predicted at baseline tended to be associated with greater decline in FVC % predicted at week 52. In the nintedanib group (n = 288), there was no evidence of an association between the extent of fibrotic ILD at baseline and decline in FVC % predicted at week 52 [r: 0.01 (95% CI: -0.11, 0.12)] or between the interplay of extent of fibrotic ILD and FVC % predicted at baseline and decline in FVC % predicted at week 52.
Conclusions: Data from the SENSCIS trial suggest that patients with SSc-ILD are at risk of ILD progression and benefit from nintedanib largely irrespective of their extent of fibrotic ILD at baseline.
Study registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, https://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02597933.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; pulmonary fibrosis; vital capacity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Elhai M, Meune C, Boubaya M. et al. Mapping and predicting mortality from systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1897–905. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann-Vold AM, Fretheim H, Halse AK. et al. Tracking impact of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in a complete nationwide cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019;200:1258–66. - PubMed
-
- Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S. et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;177:1248–54. - PubMed
-
- Moore OA, Goh N, Corte T. et al. Extent of disease on high-resolution computed tomography lung is a predictor of decline and mortality in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology 2013;52:155–60. - PubMed

