Cerebral perfusion in untreated, controlled, and uncontrolled hypertension
- PMID: 36113055
- PMCID: PMC7613835
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X221124644
Cerebral perfusion in untreated, controlled, and uncontrolled hypertension
Abstract
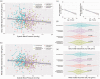
This study evaluated the association between systemic arterial blood pressure and cerebral perfusion in 740 participants of the UK's largest tri-ethnic study with measurements of cerebral blood flow (CBF) performed using arterial spin labelling MRI. A significant negative correlation between blood pressure, age and CBF was observed across the patient cohort. The lowest CBF values were recorded in the group of patients with hypertension that were prescribed with anti-hypertensive drugs, but uncontrolled on medication. These findings confirm that hypertension is associated with reduced cerebral perfusion and highlight the importance of blood pressure control for the benefit of maintaining brain blood flow.
Keywords: Cerebral blood flow; MRI; brain; hypertension; perfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: AVG is a founder and Chief Scientific Officer for Afferent Medical Solutions. XG is a founder and shareholder of Gold Standard Phantoms, a company producing ASL perfusion phantoms. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

