Cancer cell autophagy, reprogrammed macrophages, and remodeled vasculature in glioblastoma triggers tumor immunity
- PMID: 36113478
- PMCID: PMC9580613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.014
Cancer cell autophagy, reprogrammed macrophages, and remodeled vasculature in glioblastoma triggers tumor immunity
Abstract
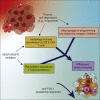
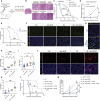
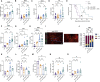
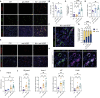
Glioblastoma (GBM) is poorly responsive to therapy and invariably lethal. One conceivable strategy to circumvent this intractability is to co-target distinctive mechanistic components of the disease, aiming to concomitantly disrupt multiple capabilities required for tumor progression and therapeutic resistance. We assessed this concept by combining vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway inhibitors that remodel the tumor vasculature with the tricyclic antidepressant imipramine, which enhances autophagy in GBM cancer cells and unexpectedly reprograms immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages via inhibition of histamine receptor signaling to become immunostimulatory. While neither drug is efficacious as monotherapy, the combination of imipramine with VEGF pathway inhibitors orchestrates the infiltration and activation of CD8 and CD4 T cells, producing significant therapeutic benefit in several GBM mouse models. Inclusion up front of immune-checkpoint blockade with anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in eventually relapsing tumors markedly extends survival benefit. The results illustrate the potential of mechanism-guided therapeutic co-targeting of disparate biological vulnerabilities in the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: VEGF inhibitors; anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade; glioblastoma immunotherapy; high endothelial venules; histamine receptor signaling; immunostimulatory autophagy; multi-targeted cancer therapy; remodeling tumor vasculature; reprogramming immunosuppressive macrophages; repurposing tricyclic antidepressants.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.H. is also a Director of Opna Bio, a Lausanne-based biotech startup that has no relationship to or vested interest in this manuscript.
Figures
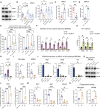
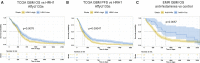
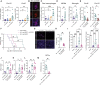

Comment in
-
Advances in co-opting anti-depressant drugs in glioma therapy.Cell Rep Med. 2022 Dec 20;3(12):100837. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100837. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 36543105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akkari L., Bowman R.L., Tessier J., Klemm F., Handgraaf S.M., de Groot M., Quail D.F., Tillard L., Gadiot J., Huse J.T., et al. Dynamic changes in glioma macrophage populations after radiotherapy reveal CSF-1R inhibition as a strategy to overcome resistance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020;12:eaaw7843. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw7843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allen E., Jabouille A., Rivera L.B., Lodewijckx I., Missiaen R., Steri V., Feyen K., Tawney J., Hanahan D., Michael I.P., Bergers G. Combined antiangiogenic and anti-PD-L1 therapy stimulates tumor immunity through HEV formation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017;9:eaak9679. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aak9679. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

