Serum neutralization activity declines but memory B cells persist after cure of chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 36114169
- PMCID: PMC9481596
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33035-z
Serum neutralization activity declines but memory B cells persist after cure of chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
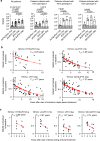
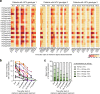
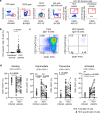
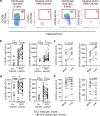
The increasing incidence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections underscores the need for an effective vaccine. Successful vaccines to other viruses generally depend on a long-lasting humoral response. However, data on the half-life of HCV-specific responses are lacking. Here we study archived sera and mononuclear cells that were prospectively collected up to 18 years after cure of chronic HCV infection to determine the role of HCV antigen in maintaining neutralizing antibody and B cell responses. We show that HCV-neutralizing activity decreases rapidly in potency and breadth after curative treatment. In contrast, HCV-specific memory B cells persist, and display a restored resting phenotype, normalized chemokine receptor expression and preserved ability to differentiate into antibody-secreting cells. The short half-life of HCV-neutralizing activity is consistent with a lack of long-lived plasma cells. The persistence of HCV-specific memory B cells and the reduced inflammation after cure provide an opportunity for vaccination to induce protective immunity against re-infection.
© 2022. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the care and treatment of persons diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Geneva: World Health Organization; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. ISBN 978-92-4-155034-5 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

