Imaging features of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas and its differentiation from conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36114217
- PMCID: PMC9481632
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19517-6
Imaging features of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas and its differentiation from conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
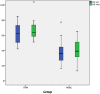
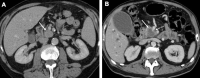
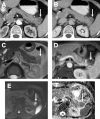
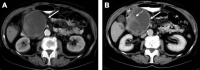
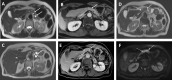
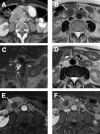
Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasms (ITPN) are rare pancreatic tumors (< 1% of exocrine neoplasms) and are considered to have better prognosis than classical pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The present study aimed to evaluate imaging features of ITPN in computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. We performed monocentric retrospective analysis of 14 patients with histopathologically verified ITPN, operated in 2003-2018. Images were available for 12 patients and were analysed independently by two radiologists, blinded to reports. Imaging features were compared to a matched control group consisting of 43 patients with PDAC, matched for sex and age. Histopathologic analysis showed invasive carcinoma component in all ITPN patients. CT-attenuation values of ITPN were higher in arterial and venous phases (62.3 ± 14.6 HU and 68 ± 15.6 HU) than in unenhanced phase (39.2 ± 7.9 HU), compatible with solid lesion enhancement. Compared to PDAC, ITPN lesions had significantly higher HU-values in both arterial and venous phases (arterial and venous phases, p < 0.001). ITPN were significantly larger than PDAC (4.1 ± 2.0 cm versus 2.6 ± 0.84 cm, p = 0.021). ITPN lesions were more often well-circumscribed (p < 0.002). Employing a multiple logistic regression analysis with forward stepwise method, higher HU density in the arterial phase (p = 0.012) and well-circumscribed lesion margins (p = 0.047) were found to be significant predictors of ITPN versus PDAC. Our study identified key imaging features for differentiation of ITPN and PDAC. Isodensity or moderate hypodensity and well-circumscribed margins favor the diagnosis of ITPN over PDAC. Being familiar with CT-features of these rare pancreatic tumors is essential for radiologists to accelerate the diagnosis and narrow the differentials.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multimodality imaging studies of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019 Jul;25(4):251-256. doi: 10.5152/dir.2019.18215. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31147310 Free PMC article.
-
An extremely rare case who underwent total remnant pancreatectomy due to recurrent pancreatic metastasis of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr;12(2):153-159. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0913-x. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30284703
-
Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN) of the pancreas associated with an invasive component: a case report with review of the literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Nov 16;15(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1267-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29145864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative characterization of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN) of the pancreas and associated invasive adenocarcinoma.Mod Pathol. 2022 Dec;35(12):1929-1943. doi: 10.1038/s41379-022-01143-2. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Mod Pathol. 2022. PMID: 36056133 Free PMC article.
-
A case of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in a branch duct: a rare case report and literature review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 13;21(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01744-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33849435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intraductal Tubulopapillary Neoplasm Diagnosed Before Surgery: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Mar 30;15(3):e36932. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36932. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37131554 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic mixed acinar-neuroendocrine carcinoma with intraductal growth: A case report with radiologic-pathologic correlations.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Oct 9;18(12):4422-4430. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.09.032. eCollection 2023 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37929047 Free PMC article.
-
A case of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growing within the pancreatic duct mimicking an intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr;18(2):376-382. doi: 10.1007/s12328-025-02098-y. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39910028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise N. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System. 4. IARC Press; 2010.
-
- Basturk O, Adsay V, Askan G, Dhall D, Zamboni G, Shimizu M, Cymes K, Carneiro F, Balci S, Sigel C, Reid MD, Esposito I, Baldaia H, Allen P, Klöppel G, Klimstra DS. Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 33 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010;41:313–325. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi H, Shimizu M, Ban S, Koyama I, Hatori T, Fujita I, Yamamoto M, Kawamura S, Kobayashi M, Ishida K, Morikawa T, Motoi F, Unno M, Kanno A, Satoh K, Shimosegawa T, Orikasa H, Watanabe T, Nishimura K, Ebihara Y, Koike N, Furukawa T. Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas distinct from pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009;33:1164–1172. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181a162e5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Date K, Okabayashi T, Shima Y, Iwata J, Sumiyoshi T, Kozuki A, Morita S, Hata Y, Noda Y, Nishioka A, Matsumoto M. Clinicopathological features and surgical outcomes of intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: A systematic review. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2016;401:439–447. doi: 10.1007/s00423-016-1391-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

