Knock-out of 5-lipoxygenase in overexpressing tumor cells-consequences on gene expression and cellular function
- PMID: 36114329
- PMCID: PMC9842508
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-022-00531-9
Knock-out of 5-lipoxygenase in overexpressing tumor cells-consequences on gene expression and cellular function
Abstract
5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO), the central enzyme in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes, is frequently expressed in human solid malignancies even though the enzyme is not present in the corresponding healthy tissues. There is little knowledge on the consequences of this expression for the tumor cells regarding gene expression and cellular function. We established a knockout (KO) of 5-LO in different cancer cell lines (HCT-116, HT-29, U-2 OS) and studied the consequences on global gene expression using next generation sequencing. Furthermore, cell viability, proliferation, migration and multicellular tumor spheroid (MCTS) formation were studied in these cells. Our results show that 5-LO influences the gene expression and cancer cell function in a cell type-dependent manner. The enzyme affected genes involved in cell adhesion, extracellular matrix formation, G protein signaling and cytoskeleton organization. Furthermore, absence of 5-LO elevated TGFβ2 expression in HCT-116 cells while MCP-1, fractalkine and platelet-derived growth factor expression was attenuated in U-2 OS cells suggesting that tumor cell-derived 5-LO shapes the tumor microenvironment. In line with the gene expression data, KO of 5-LO had an impact on cell proliferation, motility and MCTS formation. Interestingly, pharmacological inhibition of 5-LO only partly mimicked the KO suggesting that also noncanonical functions are involved.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


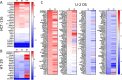

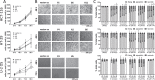



Similar articles
-
The role of human 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) in carcinogenesis - a question of canonical and non-canonical functions.Oncogene. 2024 May;43(18):1319-1327. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03016-1. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38575760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human 5-lipoxygenase regulates transcription by association to euchromatin.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;203:115187. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115187. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35878796
-
IL-4 determines eicosanoid formation in dendritic cells by down-regulation of 5-lipoxygenase and up-regulation of 15-lipoxygenase 1 expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5152-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091076998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11320251 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic Cancer Cells Suppress 5-Lipoxygenase in Tumor-Associated Macrophages.J Immunol. 2018 Jan 15;200(2):857-868. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700609. Epub 2017 Dec 11. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29229677
-
Beyond leukotriene formation-The noncanonical functions of 5-lipoxygenase.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019 Jun;142:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019. PMID: 30930090 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, Characterization, and Investigation of Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Thiourea Derivatives of Naproxen.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 19;16(1):1. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010001. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38276479 Free PMC article.
-
The role of human 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) in carcinogenesis - a question of canonical and non-canonical functions.Oncogene. 2024 May;43(18):1319-1327. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03016-1. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38575760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-dimensional growth reveals fine-tuning of 5-lipoxygenase by proliferative pathways in cancer.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Feb 27;6(5):e202201804. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201804. Print 2023 May. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 36849252 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and In Vitro Biological Evaluation of p-Carborane-Based Di-tert-butylphenol Analogs.Molecules. 2023 Jun 4;28(11):4547. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114547. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37299023 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxygenases at the Intersection of Infection and Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

