InterMob: a 24-month randomised controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of an intervention including behavioural change techniques and free transport versus an intervention including air pollution awareness-raising on car use reduction among regular car users living in Grenoble, France
- PMID: 36114537
- PMCID: PMC9482286
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-14099-4
InterMob: a 24-month randomised controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of an intervention including behavioural change techniques and free transport versus an intervention including air pollution awareness-raising on car use reduction among regular car users living in Grenoble, France
Abstract
Background: Frequent car use contributes to health and environmental issues such as air pollution, climate change and obesity. Active and sustainable mobility (bike, walk, public transport, car sharing) may address these issues. Different strategies have been implemented in past research, involving hard levers, aimed at modifying the economical or geographical context (e.g., free public transport), and soft levers, aimed at modifying psychological processes (e.g., personalised transport advice). However, few studies have combined both hard and soft levers. In addition, few have used robust methodologies (e.g., randomised controlled trials), followed behavioural changes in the long-term, and been anchored in behaviour change theories. InterMob aims to address these limits by implementing a 24-month randomised controlled trial including hard and soft levers. The objectives of InterMob are to a) evaluate the effectiveness of an experimental arm versus an active controlled arm, and b) identify the processes of mobility change.
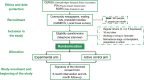
Methods: Regular car users living in Grenoble (N = 300) will be recruited and randomised to one of the two arms. The experimental arm consists in a six-month intervention combining hard levers (free access to transport/bikes), and soft levers (e.g., personalised transport advice). The control arm consists in a six-month intervention aimed at raising awareness on air pollution and its health effects. Both arms will include eight evaluation weeks (spread out over 24 months) based on a GPS, an accelerometer, and a pollution sensor. Moreover, participants will complete mobility logbooks and surveys measuring psychological constructs, socio-economical, and socio-spatial characteristics.
Discussion: InterMob will assess the effectiveness of two interventions aimed at reducing car use within regular car users in the short-, mid- and long-term. Moreover, InterMob will allow to better understand the psychological processes of behaviour change, and the socio-economical and geographical conditions under which the intervention is efficient in reducing car use. Finally, the benefits of mobility change in terms of physical activity, quality of life, and exposure to pollution will be quantified.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov : NCT05096000 on 27/10/2021 (retrospectively registered).
Keywords: Active mobility; Air pollution; Behaviour change; Car use; Daily mobility; Health; Psychology; RCT; Spatial organisation; Sustainable mobility.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Free public transport and free access to conventional or electric bicycles (for the experimental arm) will be financed by Grenoble-Alpes Métropole, SMMAG and Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes that are key players in mobility, health, and environmental issues in Grenoble metropolitan area.
Figures




References
-
- CITEPA . Gaz à effet de serre et polluants atmosphériques. Bilans des émissions en France de 1990 à 2018. CITEPA; 2020. pp. 1–459.
-
- WHO . Ambient (outdoor) air pollution. World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- Chakrabarti S, Shin EJ. Automobile dependence and physical inactivity: insights from the California household travel survey. J Transp Health. 2017;6:262–271. doi: 10.1016/j.jth.2017.05.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

