Cross-sectional study on the association of periodontitis with arterial hypertension in the Hamburg City Health Study
- PMID: 36114562
- PMCID: PMC9479239
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-022-00811-y
Cross-sectional study on the association of periodontitis with arterial hypertension in the Hamburg City Health Study
Abstract
Aim: Aim of this study was to investigate the association between periodontitis and arterial hypertension, both of which show correlations with classical cardiovascular risk factors and inflammatory activity.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional analysis of data from a large population-based health survey (the Hamburg City Health Study, HCHS) including 5934 participants with complete periodontal examination and blood pressure data, of whom 5735 had medical records regarding anti-hypertensive medication, was performed. Probing depths, gingival recessions, bleeding on probing (BOP), dental plaque, and decayed-missing-filled teeth (DMFT) indices were recorded as measures of oral health. Clinical attachment loss (CAL) per tooth was calculated and periodontitis was staged into three groups (no/mild, moderate, severe). Arterial hypertension was diagnosed based on the participants' medication history and systolic and diastolic blood pressure values. Logistic regression models were constructed accounting for a set of potential confounders (age, sex, smoking, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, educational level, alcohol intake) and high sensitivity-C-reactive protein (hsCRP).
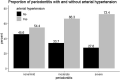
Results: The odds of arterial hypertension increased significantly along with periodontitis severity (OR for severe periodontitis: 2.19; 95% CI 1.85-2.59; p < 0.001; OR for moderate periodontitis: 1.65; 95% CI 1.45-1.87; p < 0.001). Participants with moderate or severe periodontitis also had significantly higher age- and sex-adjusted odds of arterial hypertension, which was slightly weakened when additionally adjusted for BMI, diabetes, smoking, educational level, and alcohol intake (OR for severe PD: 1.28, 95% CI 1.04-1.59, p = 0.02; OR for moderate PD: 1.30, 95% CI 1.11-1.52, p = 0.001). The fraction of participants with undertreated hypertension (untreated and poorly controlled hypertension) was considerably larger in participants with severe periodontitis than in those with no/mild periodontitis (50.1% vs. 37.4% for no/mild periodontitis).
Conclusions: The study shows an association between periodontitis and arterial hypertension that is independent of age, sex, diabetes, BMI, smoking, educational level, and alcohol intake. In addition, undertreatment of hypertension was more common in people with severe periodontitis compared with periodontally more healthy people.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Cross-sectional studies; Epidemiology; Hypertension; Periodontitis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between an Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Score and Periodontitis-Evidence from the Population-Based Hamburg City Health Study.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 21;15(14):3235. doi: 10.3390/nu15143235. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37513653 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis, dental plaque, and atrial fibrillation in the Hamburg City Health Study.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 22;16(11):e0259652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259652. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34807935 Free PMC article.
-
Association between periodontitis and metabolic syndrome in the Hamburg City Health Study.J Periodontol. 2022 Aug;93(8):1150-1160. doi: 10.1002/JPER.21-0464. Epub 2022 Jan 27. J Periodontol. 2022. PMID: 34967009
-
Cross-sectional analysis of the association of periodontitis with carotid intima media thickness and atherosclerotic plaque in the Hamburg City health study.J Periodontal Res. 2022 Aug;57(4):824-834. doi: 10.1111/jre.13021. Epub 2022 Jun 8. J Periodontal Res. 2022. PMID: 35675038
-
Periodontal disease, hypertension, and blood pressure among older adults in Puerto Rico.J Periodontol. 2013 Feb;84(2):203-11. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110748. Epub 2012 May 1. J Periodontol. 2013. PMID: 22548584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The correlation between periodontitis and uncontrolled hypertension is mediated by inflammatory markers: results from a cross-sectional study of urban elderly population in southeast China.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Nov 24;23(1):919. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03680-x. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38001437 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis is associated with stroke.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 6;21(1):697. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04545-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37803341 Free PMC article.
-
Association between an Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Score and Periodontitis-Evidence from the Population-Based Hamburg City Health Study.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 21;15(14):3235. doi: 10.3390/nu15143235. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37513653 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontal Disease and Its Association with Metabolic Syndrome-A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 21;24(16):13011. doi: 10.3390/ijms241613011. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
General health status of a sample of patients with periodontitis in a Spanish university dental clinic: A case-control study.J Clin Exp Dent. 2024 Oct 1;16(10):e1224-e1232. doi: 10.4317/jced.62102. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Clin Exp Dent. 2024. PMID: 39544217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou B, Carrillo-Larco RM, Danaei G, Riley LM, Paciorek CJ, Stevens GA, Gregg EW, Bennett JE, Solomon B, Singleton RK, Sophiea MK. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398(10304):957–980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials