CT patterns and serial CT Changes in lung Cancer patients post stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT)
- PMID: 36114585
- PMCID: PMC9482277
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-022-00491-1
CT patterns and serial CT Changes in lung Cancer patients post stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT)
Abstract
Background: To evaluate computed tomography (CT) patterns of post-SBRT lung injury in lung cancer and identify time points of serial CT changes.
Materials and methods: One hundred eighty-three tumors in 170 patients were evaluated on sequential CTs within 29 months (median). Frequencies of post-SBRT CT patterns and time points of initiation and duration were assessed. Duration of increase of primary lesion or surrounding injury without evidence of local recurrence and time to stabilization or local recurrence were evaluated.
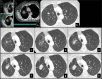
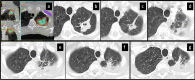
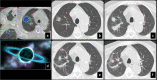
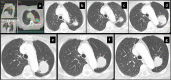
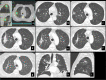
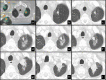
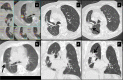
Results: Post-SBRT CT patterns could overlap in the same patient and were nodule-like pattern (69%), consolidation with ground glass opacity (GGO) (41%), modified conventional pattern (39%), peribronchial/patchy consolidation (42%), patchy GGO (24%), diffuse consolidation (16%), "orbit sign" (21%), mass-like pattern (19%), scar-like pattern (15%) and diffuse GGO (3%). Patchy GGO started at 4 months post-SBRT. Peribronchial/patchy consolidation and consolidation with GGO started at 4 and 5 months respectively. Diffuse consolidation, diffuse GGO and orbit sign started at 5, 6 and 8 months respectively. Mass-like, modified conventional and scar-like pattern started at 8, 12 and 12 months respectively. Primary lesion (n = 11) or surrounding injury (n = 85) increased up to 13 months. Primary lesion (n = 119) or surrounding injury (n = 115) started to decrease at 4 and 9 months respectively. Time to stabilization was 20 months. The most common CT pattern at stabilization was modified conventional pattern (49%), scar-like pattern (23%) and mass-like pattern (12%). Local recurrence (n = 15) occurred at a median time of 18 months.
Conclusion: Different CT patterns of lung injury post-SBRT appear in predictable time points and have variable but predictable duration. Familiarity with these patterns and timeframes of appearance helps differentiate them from local recurrence.
Keywords: CT patterns; Computed tomography; Lung cancer; Radiation induced lung injury; Stereotactic body radiotherapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early and late lung radiographic injury following stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT).Lung Cancer. 2010 Jul;69(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Lung Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19910075
-
CT appearance of radiation injury of the lung and clinical symptoms after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancers: are patients with pulmonary emphysema also candidates for SBRT for lung cancers?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Oct 1;66(2):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.05.008. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 16904838
-
Assessment and agreement of the CT appearance pattern and its severity grading of radiation-induced lung injury after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 4;13(10):e0204734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204734. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30286105 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancer: a timeline and pattern of CT changes.Eur J Radiol. 2011 Jul;79(1):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.10.029. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Eur J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 19954913 Review.
-
Can high-risk CT features suggest local recurrence after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2020 Jun;127:108978. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108978. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32298960 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spectrum of Imaging Patterns of Lung Cancer following Radiation Therapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;13(20):3283. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203283. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with cavity formation after stereotactic body radiation therapy for peripheral early-stage lung cancer.Radiol Med. 2024 Mar;129(3):507-514. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01766-2. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 38286868
-
Chronic progressive pulmonary aspergillosis within the irradiated field after stereotactic body radiotherapy: two case reports.Int Cancer Conf J. 2025 Jan 21;14(2):113-118. doi: 10.1007/s13691-025-00744-3. eCollection 2025 Apr. Int Cancer Conf J. 2025. PMID: 40160886
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

