Burden and trends of brain and central nervous system cancer from 1990 to 2019 at the global, regional, and country levels
- PMID: 36115969
- PMCID: PMC9482735
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-022-00965-5
Burden and trends of brain and central nervous system cancer from 1990 to 2019 at the global, regional, and country levels
Abstract
Background: Regularly updated epidemiological data on the burden of brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers are important in the prioritization of research and the allocation of resources. This study aimed to investigate incidence, mortality, disability, and trends in brain and CNS cancers between 1990 and 2019.
Methods: Epidemiological data, including the cancer incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years(DALYs), age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), and age-standardized DALY rate (per 100,000 population) stratified by region, country, sex, and age group were retrieved and extracted using the Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) query tool.
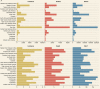
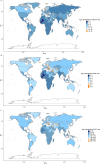
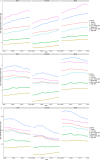
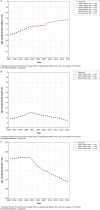
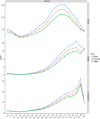
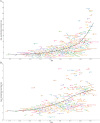
Results: In 2019, there were 347,992(262,084-388,896) global cases of brain and CNS cancers, which showed a significant increase (94.35%) from the period between 1990 to 2019. The global ASIR in 2019 was 4.34 (3.27-4.86) per 100, 000 population, which showed an increasing trend for the years 1990-2019 (13.82% [-27.27-32.83]). In 2019, there were 246,253 (185,642-270,930) global deaths caused by brain and CNS cancers, which showed a significant increase (76.36%) during the study period. The global ASMR in 2019 was 3.05(2.29-3.36) per 100, 000 population, which did not change significantly over the study period (-1.19% [-36.79-13.86]). In 2019, there were 8,659,871 DALYs, which was a 109.04% increase compared with 1990. Similarly, during 1990-2019, the age-standardized DALY rate decreased by 10.39%. Additionally, 76.60% of the incident cases, 72.98% of the deaths, and 65.16% of the DALYs due to brain and CNS cancers occurred in the high-income and upper-middle-income regions.
Conclusions: In conclusion, brain and CNS cancers remain a major public health burden, particularly in high-income regions. The global incidence, deaths, and DALYs of brain and CNS cancers were shown to have increased significantly from 1990 to 2019. The global ASIR kept rising steadily, while the ASMR and age-standardized DALY rate declined over the past three decades.
Keywords: Brain cancer; Central nervous system cancer; Disability-adjusted life years; Incidence; Mortality.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

