Oxidative modification of HDL by lipid aldehydes impacts HDL function
- PMID: 36116503
- PMCID: PMC9670862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109397
Oxidative modification of HDL by lipid aldehydes impacts HDL function
Abstract
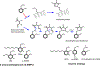
Reduced levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol correlate with increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and HDL performs functions including reverse cholesterol transport, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, and suppression of inflammation, that would appear critical for cardioprotection. However, several large clinical trials utilizing pharmacologic interventions that elevated HDL cholesterol levels failed to provide cardioprotection to at-risk individuals. The reasons for these unexpected results have only recently begun to be elucidated. HDL cholesterol levels and HDL function can be significantly discordant, so that elevating HDL cholesterol levels may not necessarily lead to increased functional capacity, particularly under conditions that cause HDL to become oxidatively modified, resulting in HDL dysfunction. Here we review evidence that oxidative modifications of HDL, including by reactive lipid aldehydes generated by lipid peroxidation, reduce HDL functionality and that dicarbonyl scavengers that protect HDL against lipid aldehyde modification are beneficial in pre-clinical models of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; HDL; Isolevuglandins; Lipid aldehydes; Malondialdehyde; apoA1.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR, High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study, The American journal of medicine 62(5) (1977) 707–14. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Kannel WB, Prevalence of coronary heart disease in the Framingham Offspring Study: role of lipoprotein cholesterols, The American journal of cardiology 46(4) (1980) 649–54. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Gotto AM, HDL Cholesterol and Protective Factors in Atherosclerosis, Circulation 109(23_suppl_1) (2004) III-8-III–14. - PubMed
-
- Badimon JJ, Badimon L, Galvez A, Dische R, Fuster V, High density lipoprotein plasma fractions inhibit aortic fatty streaks in cholesterol-fed rabbits, Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology 60(3) (1989) 455–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

