Network pharmacology unveils spleen-fortifying effect of Codonopsis Radix on different gastric diseases based on theory of "same treatment for different diseases" in traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 36117498
- PMCID: PMC9476800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2020.12.005
Network pharmacology unveils spleen-fortifying effect of Codonopsis Radix on different gastric diseases based on theory of "same treatment for different diseases" in traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
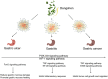
Objective: "Same treatment for different diseases" is a unique treatment strategy under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory. Codonopsis Radix (Codonopsis pilosula, Dangshen in Chinese) with spleen-fortifying effect was employed to understand the strategy of "Same treatment for different diseases", based on its common mechanism in the treatment of gastric diseases including gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer via network pharmacology research.
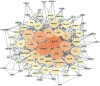
Methods: Network pharmacology research methods were used to analyze the interaction network and potential mechanisms of Dangshen in treating gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer. The active components and their target proteins of Dangshen were integrated from TCMSP, BATMAN-TCM databases. The targets of gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer were collected through GeneCards, PubMed, TDD and DisGeNET Database. Through screening, the key components and the key targets of Dangshen in treating gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer were obtained. After KEGG pathway analysis and GO analysis, the important pathways and biological processes were analyzed.
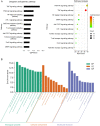
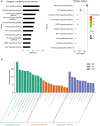
Results: Through data and literature mining, the common and specific pharmaceutical effects and mechanism of Dangshen were summarized in these three gastric lesions. It was shown that Dangshen mainly acted on gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer through the overall regulation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. With the development of the disease, it will gradually increase the control of inflammation through TNF, NF-κB and other inflammation-related signaling pathways to reduce inflammatory damage. For tumorigenesis, it pays more attention to inhibiting the ErbB signaling pathways to reduce the proliferation and migration of tumor cells. In addition, Dangshen's regulation of HIF-1 signaling pathway may also be beneficial for the treatment of gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer.
Conclusion: Dangshen achieves spleen-fortifying effect on gastric diseases including gastric ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer through multiple targets in multiple pathways, especially PI3K-AKT pathway and HIF-1 pathway. It could provide a scientific basis for understanding the strategy of "Same treatment for different diseases" in traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: Codonopsis Radix; gastric cancer; gastric ulcer; gastritis; network pharmacology; same treatment for different diseases; spleen-fortifying effect.
© 2020 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics to Explore the Effects of Dangshen (Codonopsis pilosula) Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Validation Based on the Active Compound Luteolin.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Mar 1;17:659-673. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S386941. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36883114 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology reveals the mechanism of the herbal pairing of Codonopsis Pilosula (Franch.) Nannf and Astragalus Membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge on chronic heart failure.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):7942-7959. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1469. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353081
-
[Effect and mechanism of Jingqi Yukui Capsules on gastric ulcer mucosa healing quality: based on network pharmacology and animal experiment].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Mar;47(5):1350-1358. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211117.702. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35343164 Chinese.
-
Radix Codonopsis: a review of anticancer pharmacological activities.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1498707. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1498707. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39840099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring pharmaphylogeny from multiple perspectives: a case study on Lithospermeae.Sci Rep. 2023 May 11;13(1):7636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34830-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37169837 Free PMC article.
-
Study on complications of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 29;13:941098. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.941098. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albina J., Mastrofrancesco B., Vessella J., Louis C., Henry W., Reichner J. HIF-1 expression in healing wounds: HIF-1alpha induction in primary inflammatory cells by TNF-alpha. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology. 2001;281(6):C1971–1977. - PubMed
-
- Arab H., Salama S., Eid A., Kabel A., Shahin N. Targeting MAPKs, NF-kappaB, and PI3K/AKT pathways by methyl palmitate ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2019;234(12):22424–22438. - PubMed
-
- Aziz N., Kim M., Cho J. Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2018;225:342–358. - PubMed
-
- Bai R., Li W., Li Y., Ma M., Wang Y., Zhang J., Hu F. Cytotoxicity of two water-soluble polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. var. modesta (Nannf.) L. T. Shen against human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells and its mechanism. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2018;120(Pt B):1544–1550. - PubMed
-
- Blouin C., Page E., Soucy G., Richard D. Hypoxic gene activation by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages: Implication of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Blood. 2004;103(3):1124–1130. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

