Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Patients: Results From an Injection Technique Targeting the Index Lesion in the Prostate Gland
- PMID: 36117970
- PMCID: PMC9478858
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.931867
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Patients: Results From an Injection Technique Targeting the Index Lesion in the Prostate Gland
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the accuracy of nodal staging in patients with prostate cancer (PCa) when 99 m Tc-nanocolloid radiotracer is injected into an index lesion (IL).
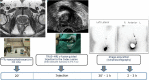
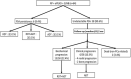
Methods: This prospective study was conducted at our institution between June 2016 and October 2020. It included 64 patients with localized PCa with at least a 5% possibility for lymph node involvement in the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center nomogram, suitable for surgical treatment. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with IL and were pathologically confirmed. The day before surgery, transrectal ultrasound-guided injection (TRUS) of 99 m Tc-nanocolloid into the IL was performed. Surgical procedures included radical prostatectomy (RP), sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), and extended pelvic lymphadenectomy (ePLND). Analysis was performed, including histopathological findings of RP, ePLND, and SLNB. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), false negative (FN), false positive (FP), diagnostic yield, and non-diagnostic rate were calculated.
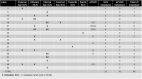
Results: A total of 1,316 lymph nodes were excised, including 1,102 from the ePLND (83.7%) and 214 (16.3%) sentinel lymph nodes (SLN). 26 SLN were dissected outside the ePLND template. The final pathology demonstrated 46 (3.5%) lymph node metastasis, 31 (67.4%) in the SLNB and 15 (32.6%) in the non-SLN ePLND. At the patient level, 18 (28.1%) patients had pN1. With a mean follow-up of 33.1 months, 4/19 (21.1%) pN1 patients had undetectable PSA, and 3/19 (15.8%) had a PSA < 0.1 ng/mL. Lymph node dissection included 20.6 lymph nodes per patient (IQR 15-24.2), with 3.3 SLNB nodes per patient (IQR 2-4.2). PPV and NPV were 100 and 97.8%, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity were 94.4 and 100%, respectively. FN was 5.5% and FP was 4.3%. Diagnostic yields were 95.3% and the non-diagnostic rate was 4.7%.
Conclusion: Radiotracer injection into the prostate IL offers promising results for staging purposes in cases in which ePLND is considered. Negative SLNB is a predictor of negative ePLND. Patients with a limited burden of nodal metastasis have a significant chance of remaining free of biochemical recurrence at mid-term follow-up.
Keywords: pelvic lymph node dissection; prostate cancer; radio-guided surgery; sentinel lymph node; tracer deposition.
Copyright © 2022 Fumadó, Abascal, Mestre-Fusco, Vidal-Sicart, Aguilar, Juanpere and Cecchini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Monserrat-Montfort JJ, Vera-Donoso C, Martinez-Sarmiento M, Betancourt-Hernández J, Avargues A, Vera-Pinto V, et al. MP47-02 sentinel node technique in radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer patients: toward an individualized lymphadenectomy. J Urol. (2017) 197:e628.
-
- Kim KH, Lim SK, Kim HY, Shin TY, Lee JY, Choi YD, et al. Extended vs standard lymph node dissection in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer: a propensity-score-matching analysis. BJU Int. (2013) 112:216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

