Efficacy and Safety of Gegen Qinlian Decoction for Pediatric Diarrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36118086
- PMCID: PMC9477636
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4887259
Efficacy and Safety of Gegen Qinlian Decoction for Pediatric Diarrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction in the treatment of pediatric diarrhea.
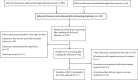
Methods: A search for relevant RCTs was performed from which a systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted. This meta-analysis was registered at INPLASY (reference number ID: INPLASY202180105).
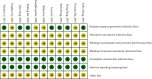
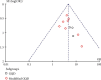
Results: (1) Eleven trials involving 1126 patients were included in the meta-analysis. (2) Two trials recorded the adverse events. (3) The meta-analysis showed that compared with the control group, the experimental group has a significantly shorter duration of diarrhea in children (MD = -18.64, 95% CI (-23.76, -13.52), P < 0.00001), duration of fever (MD = -19.43, 95% CI (-25.76, -13.11), P < 0.00001), duration of vomiting [MD = -22.51, 95% CI (-29.92, -15.09), P < 0.00001], duration of correcting dehydration (MD = -23.35, 95% CI (-35.48, -11.22), P=0.0002), and the effective rate (OR = 4.64, 95% CI (3.12, 6.90), P < 0.00001).
Conclusion: There were significant differences in the clinical efficacy in the treatment of pediatric diarrhea between the experimental and control groups. Thus, Gegen Qinlian decoction may have certain advantages in the treatment of pediatric diarrhea. In addition, we conclude the following: (1) the application of Gegen Qinlian decoction to treat this disease is recommended for >5 days. (2) We recommend conducting multicenter RCTs to avoid the impact of regional differences on the results. (3) We recommend using the unmodified Gegen Qinlian decoction, which may have better efficacy.
Copyright © 2022 Dan Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 26;14:1316269. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1316269. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38344688 Free PMC article.
-
Gegen Qinlian Decoction Combined with Conventional Western Medicine for the Treatment of Infectious Diarrhea: A Systematic Review and Trial Sequential Analysis.Complement Med Res. 2024;31(5):461-476. doi: 10.1159/000540793. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Complement Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39137735 English.
-
[Effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on gut microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Dec;47(24):6709-6719. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220721.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36604921 Chinese.
-
Exploration of the Mechanism of the Control of Coccidiosis in Chickens Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking With the Addition of Modified Gegen Qinlian Decoction.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 17;9:849518. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.849518. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35372563 Free PMC article.
-
[Differences in intestinal absorption of Gegen Qinlian Decoction between normal rats and rats with large intestinal damp-heat syndrome].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Jan;45(1):169-178. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190318.506. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237427 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Protective Application of Chinese Herbal Compounds and Formulae in Intestinal Inflammation in Humans and Animals.Molecules. 2023 Sep 26;28(19):6811. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196811. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative effectiveness and safety of Chinese medicine belly button application for childhood diarrhea: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pediatr. 2023 Aug 4;11:1180694. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1180694. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37601135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu S.-Y. Technical guideline for clinical trial design and evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine for pediatric diarrhea. Drug Evaluation Research . 2020;43(4):660–664.
-
- Zhang Y. Evidence-based evaluation of global existed diarrhea guidelines of children. China Pharmacy . 2018;29(8):1109–1116.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

