Combination of Metformin and Sorafenib Induces Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway
- PMID: 36118519
- PMCID: PMC9475364
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.76618
Combination of Metformin and Sorafenib Induces Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway
Abstract
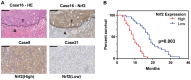
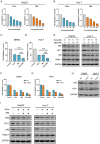
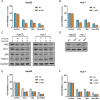
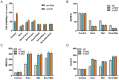
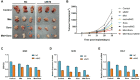
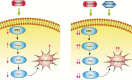
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal cancers in the world. Sorafenib is the first small-molecule multi-kinase inhibitors approved by FDA for treatment of advanced HCC. Metformin has been demonstrated to have benefit for preventing cancer progression. In human recurrent HCCs, NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) was overexpressed and associated with poor survival. Nrf2 related signaling pathway plays central role to mediate cellular resistance to sorafenib through protecting HCC cells from ferroptosis. The effect of Combination treatment for HCC cells and the intrinsic mechanism have not been reported. In this study, metformin augmented the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib for HCC through ferroptosis induction by inhibiting Nrf2 related pathway. Based on the results of Nrf2 knockdown and p62 knockdown study, the combination of sorafenib and metformin suppressed proliferation of HCC cells through p62-Keap1-Nrf2/HO1 signaling way. Size of xenografts treated with the combination of sorafenib and metformin was smaller than other groups in vivo. Moreover, the combination treatment greatly induced ferroptosis in HCC cells through inhibiting Nrf2 expression. Based on our findings, the combination treatment suppressed proliferation of HCC cells through ferroptosis induction, by p62-Keap1-Nrf2/HO1 signaling way.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2); ferroptosis; metformin; sorafenib.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF. et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS. et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

