Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio is a systemic marker of sarcopenia in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours
- PMID: 36118766
- PMCID: PMC9478187
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.963265
Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio is a systemic marker of sarcopenia in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Abstract
Background: It is well known that sarcopenia is a common risk factor in patients with gastrointestinal tumours, which may negatively affect the clinical outcome and prognosis. Recent studies suggest that serum creatinine-cystatin C (Cr/CysC) ratio may be associated with sarcopenia, but this association lacks sufficient evidence in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate whether the Cr/CysC ratio was associated with sarcopenia and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients with GIST.
Materials and methods: The study retrospectively analysed 413 patients with GIST who underwent surgical resection from January 2016 to January 2020. The serum Cr/CysC ratio was determined as a proxy for sarcopenia by comparing it with various biomarkers and Cox multifactorial analysis was used to determine the relationship between Cr/CysC ratio and prognosis.
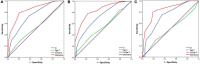
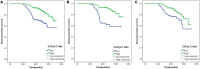
Results: Serum Cr/CysC was positively correlated with skeletal muscle area (SMA) (r = 0.256, p < 0.001), skeletal muscle index (SMI) (r = 0.300, p < 0.001), and hand grip strength (HGS) (r = 0.251, p < 0.001). The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve for sarcopenic subjects with serum Cr/CysC ratio was significantly greater than other biomarkers (Cr/CysC: 0.840, CysC: 0.732, Cr: 0.518). The optimal cut-off value for Cr/CysC was 0.65, and patients in the high Cr/CysC group had a higher 3-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) than those in the low Cr/CysC group (92.72 vs. 72.46%, p < 0.001). Cox multifactorial analysis found that the Cr/CysC ratio was an independent risk factor for RFS in GIST patients (HR = 2.143, 95% CI: 1.431-5.459, p = 0.011).
Conclusion: Serum Cr/CysC ratio has satisfactory and comparable diagnostic accuracy, and prognostic value for sarcopenia in patients with GIST. Therefore, it can be a simple and practical clinical tool to screen sarcopenia in GIST patients. However, further studies are required to validate these findings.
Keywords: gastrointestinal stromal tumors; sarcopenia; serum Cr/CysC ratio; serum creatinine; serum cystatin C.
Copyright © 2022 Ding, Guo, Sun, Chen, Yang, Tian, Lowe and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a surrogate marker for sarcopenia in patients with gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 19;22(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02093-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35045814 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the serum creatinine and cystatin C ratio for prediction of sarcopenia and prognosis in biliary tract cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul;29(7):1002-1011. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02539-7. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38683456
-
Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a surrogate marker for sarcopenia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Clin Nutr. 2021 Mar;40(3):1274-1280. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.08.010. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32863062
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of serum creatinine and cystatin C-based index for sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Age Ageing. 2024 Jan 2;53(1):afad252. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afad252. Age Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38251741
-
Estimating renal function in children: a new GFR-model based on serum cystatin C and body cell mass.Dan Med J. 2012 Jul;59(7):B4486. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22759853 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between preoperative sarcopenia and postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing gastrointestinal cancer surgery.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jul 31;16:1416569. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1416569. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39144259 Free PMC article.
-
The coexistence of myosteatosis and the creatinine/cystatin C ratio are determinants of outcomes in cholangiocarcinoma patients undergoing curative surgery.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 19;14:1233768. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1233768. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38706605 Free PMC article.
-
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and frailty in older adults: a longitudinal cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Sep 11;24(1):753. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05326-1. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39261791 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-donation assessment of cystatin C to improve prediction of pre- and post-donation GFR in potential living kidney donors.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Oct 30;39(11):1856-1866. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae065. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38479785 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Serum Creatinine/Cystatin C Ratio and Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality: Insights from NHANES.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 25;24(9):275. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2409275. eCollection 2023 Sep. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076382 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

