Efficacy of TACE+Radiofrequency Ablation+Sorafenib in the Treatment of Patients with Recurrent Liver Cancer and Construction of Prediction Model
- PMID: 36118840
- PMCID: PMC9473901
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6879035
Efficacy of TACE+Radiofrequency Ablation+Sorafenib in the Treatment of Patients with Recurrent Liver Cancer and Construction of Prediction Model
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Efficacy of TACE+Radiofrequency Ablation+Sorafenib in the Treatment of Patients with Recurrent Liver Cancer and Construction of Prediction Model.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9850243. doi: 10.1155/2023/9850243. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38124925 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: This study is aimed at exploring the efficacy of transarterial chemotherapy embolization (TACE)+radiofrequency ablation+sorafenib in the treatment of patients with recurrent liver cancer and at constructing its prediction model.
Methods: A total of 60 patients with recurrent liver cancer treated in our hospital from March 2020 to March 2022 were enrolled and divided into two groups according to treatment methods, with 30 patients in each group. Group A adopted TACE+radiofrequency ablation+sorafenib therapy while group B adopted TACE+radiofrequency ablation therapy. Clinical efficacy, complications, and adverse reactions of the two groups were observed. A total of 30 patients with nonrecurrent liver cancer in the same period were enrolled. 60 patients with recurrent liver cancer and 30 patients with nonrecurrent liver cancer were taken as the recurrence group and the nonrecurrence group, respectively. The baseline data and clinical data of the patients were queried by the Hospital Information System. The data included age, gender, Child-Pugh grade, HBV/HCV infection, portal vein tumor thrombus, degree of differentiation, vascular invasion, serum alpha fetal protein (AFP) level, number of tumors, maximum diameter of tumors, and number of nodules. The logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the independent risk factors for liver cancer recurrence. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test was used to analyze the degree of fitting between the prediction model and the standard curve. The ROC curve was used to analyze the predictive value of the model for liver cancer recurrence.
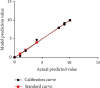
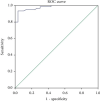
Results: The objective effective rate and disease control rate in group A (33.33% and 70.00%) were higher than those in group B (10.00% and 43.33%), and the differences were statistically significant (both P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the incidence of complications such as embolism syndrome, hand and foot skin reaction, gastrointestinal reaction, hypertension, diaphragmatic injury and bleeding, and biliary leakage and fever between the two groups (all P > 0.05). The proportions of patients in the recurrence group with portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT), medium and high degree of differentiation, combined with vascular invasion, serum AFP level ≥ 400 ng/dL, multiple tumors, maximum tumor diameter ≥ 5 cm, combined with cirrhosis, and polynodules were all higher than those in the nonrecurrence group; the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). Complication of PVTT, the degree of medium and high differentiation, and the maximum tumor diameter ≥ 5 cm were independent risk factors for recurrence of liver cancer (all P < 0.05). The prediction model of liver cancer recurrence was obtained by multiple regression analysis, P = 1/[1 + e -(-5.441 + 6.154∗PVTT + 3.475∗differentiateddegree + 3.001∗maximumdiameteroftumor)]. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed that χ 2 = 1.558 (P = 0.992). According to the ROC curve analysis, the AUC, SE, and 95% CI value of the prediction model for liver cancer recurrence were 0.977, 0.012, and 0.953-1.000, respectively.
Conclusion: TACE+radiofrequency ablation+sorafenib is effective in the treatment of recurrent liver cancer, and the prediction model established based on the risk factor has high predictive value for patients with recurrent liver cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Aimin Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Z., Jiang Y., Yuan H., et al. The trends in incidence of primary liver cancer caused by specific etiologies: results from the global burden of disease study 2016 and implications for liver cancer prevention. Journal of Hepatology . 2019;70(4):674–683. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous