The role and regulatory mechanism of m6A methylation in the nervous system
- PMID: 36118889
- PMCID: PMC9474891
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.962774
The role and regulatory mechanism of m6A methylation in the nervous system
Abstract
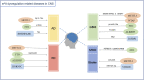
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification regulates RNA translation, splicing, transport, localization, and stability at the post-transcriptional level. The m6A modification has been reported to have a wide range of effects on the nervous system, including neurogenesis, cerebellar development, learning, cognition, and memory, as well as the occurrence and development of neurological disorders. In this review, we aim to summarize the findings on the role and regulatory mechanism of m6A modification in the nervous system, to reveal the molecular mechanisms of neurodevelopmental processes, and to promote targeted therapy for nervous system-related diseases.
Keywords: development; m6A methylation; mechanism; nervous system; neurological disorders.
Copyright © 2022 Jiang, Li, Wang, Yuan and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Role of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in central nervous system: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 Jan 25;39(1):45-59. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220236. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 36738200 Review. Chinese.
-
The Progression of N6-methyladenosine Study and Its Role in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5922. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115922. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mRNA m6A methylation in the nervous system.Cell Biosci. 2019 Aug 20;9:66. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0330-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31452869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine and Neurological Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Mar;59(3):1925-1937. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02739-0. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35032318 Review.
-
m6A modification and its role in neural development and neurological diseases.Epigenomics. 2023 Aug;15(16):819-833. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0190. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37718929 Review.
Cited by
-
Deregulating m6A regulators leads to altered RNA biology in glioma cell lines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 19:2024.10.28.620763. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.28.620763. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40894734 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
FTO-targeted siRNA delivery by MSC-derived exosomes synergistically alleviates dopaminergic neuronal death in Parkinson's disease via m6A-dependent regulation of ATM mRNA.J Transl Med. 2023 Sep 22;21(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04461-4. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37737187 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N-methyladenosine modification in acute and chronic kidney diseases.Mol Med. 2023 Dec 8;29(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00764-w. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 38066436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between epitranscriptomic RNA modifications and neurodegenerative disorders: Mechanistic insights and potential therapeutic strategies.Ibrain. 2024 Nov 11;10(4):395-426. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12183. eCollection 2024 Winter. Ibrain. 2024. PMID: 39691424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles therapy for Parkinson's disease: A systematic review of preclinical studies.World J Stem Cells. 2025 Apr 26;17(4):102421. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i4.102421. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40308882 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

